Recombinant Human Creatine Kinase, Brain
| Cat.No. : | CKB-195H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CKBBI produced inPichia Pastorisis a glycosylated polypeptide chain having an identical amino acid sequence compared to the native enzyme, purified under non-denaturing conditions and reacts with polyclonal antibodies to BB Isoenzyme in ELISA. The CKBBI is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | P.pastoris |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | Creatine Kinase BB is a cytoplasmic enzyme involved in energy homeostasis. The encoded protein reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens such as creatine phosphate. It acts as a homodimer in brain as well as in other tissues, and as a heterodimer with a similar muscle isozyme in heart. The encoded protein is a member of the ATP: guanido phosphotransferase protein family. A pseudogene of this gene has been characterized. |
| Physical Appearance : | Sterile Filtered colourless liquid formulation. |
| Formulation : | The protein (2.2 mg/ml) contains 10mM Bis-Tris-HCl pH-6.2, 50% glycerol, 0.5mM EDTA and 0.5mM DTT. |
| Stability : | CKBBI although stable at 15°C for 7 days, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity : | Greater than 95.0% as determined by: (a) Analysis by RP-HPLC. (b) Analysis by SDS-PAGE. |
| Biological Activity : | The biological activity measured by the enzymatic activity of Creatine phosphokinase procedure No.45-UV, 1IU-1 µmole creatine phosphate was 500 IU/mg at 37°C. |
| Gene Name | CKB creatine kinase, brain [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Synonyms | CKB; creatine kinase, brain; B-CK; CKBB; creatine kinase-B; EC 2.7.3.2 |
| Gene ID | 1152 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001823 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001814 |
| MIM | 123280 |
| UniProt ID | P12277 |
| Chromosome Location | 14q32.3 |
| Pathway | Arginine and proline metabolism; Metabolic pathways; Metabolism of amino acids |
| Function | ATP binding; creatine kinase activity; nucleotide binding; protein binding |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CKB-1391H | Recombinant Human CKB Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CKB-1861HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CKB Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Ckb-2129R | Recombinant Rat Ckb protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CKB-2729H | Recombinant Human Creatine Kinase, Brain, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CKB-195H | Recombinant Human Creatine Kinase, Brain | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| CKB-8079H | Active Native Human CKB protein | +Inquiry |
| CKB-46M | Native Mouse Creatine Kinase, Brain (CKB) Protein | +Inquiry |
| CKB-1177H | Native Human Creatine Kinase, Brain | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CKB-001HCL | Recombinant Human CKB cell lysate | +Inquiry |
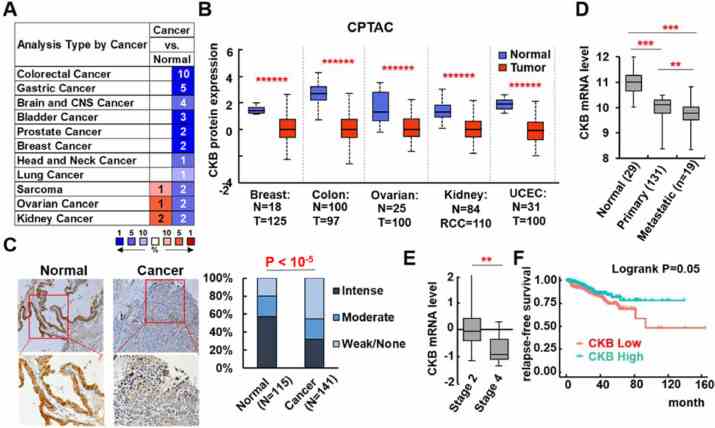
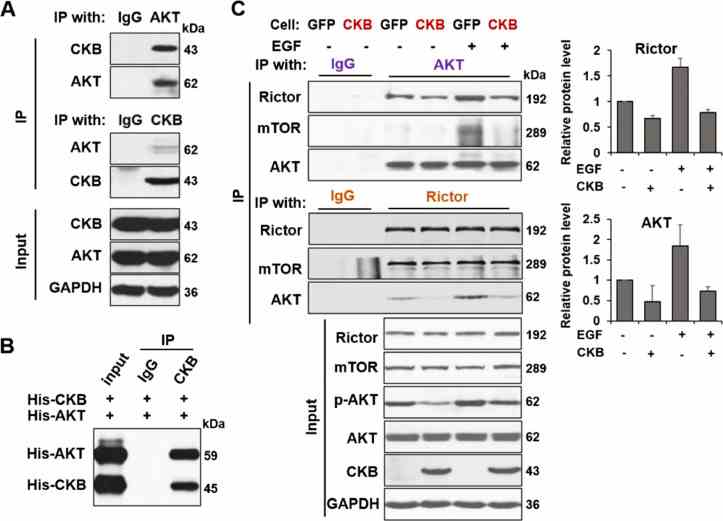
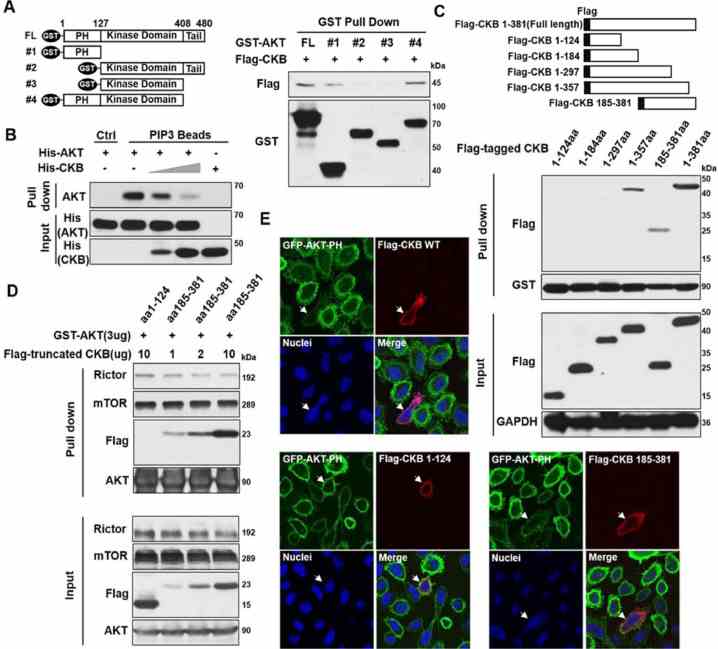
CKB inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and prostate cancer progression by sequestering and inhibiting AKT activation
Journal: Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.) PubMed ID: 34706306 Data: 2021/10/24
Authors: Zheng Wang, Mohit Hulsurkar, Wenliang Li
Article Snippet:His-tagged recombinant human AKT1 protein (#PR3878D, Invitrogen) were incubated with 0, 1 or 2ug his-tagged recombinant human CKB protein (#495H, Creative BioMart) at 4°C for 2 h on a rotating mixer.. 40μL of PIP3 or control resin beads slurry (#PB345a, Echelon) were washed with PBS and added to each tube.40μL of PIP3 or control resin beads slurry (#PB345a, Echelon) were washed with PBS and added to each tube.
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All CKB Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CKB Products
Required fields are marked with *



