Deubiquitinating Enzymes (DUBs)
Related Symbol Search List
- ATG4A
- ATG4B
- CYLD
- OTUB1
- OTUB2
- OTUD3
- OTUD7B
- OTULIN
- SENP1
- SENP2
- SENP8
- STAMBP
- TNFAIP3
- UCHL1
- UCHL3
- USP1
- USP14
- USP19
- USP25
- USP28
- USP5
- USP51
- USP7
- USP8
- USP9X
- WDR48
- YOD1
- ZRANB1
Immunology Background
About Deubiquitinating Enzymes (DUBs)
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUB), also known as deubiquitinating peptidases, deubiquitinating isopeptidases, deubiquitinases, ubiquitin proteases, ubiquitin hydrolases, or ubiquitin isopeptidases, are a large class of proteases that cleave ubiquitin from proteins. Ubiquitin attaches to proteins and regulates protein degradation, coordinates protein cellular localization, activates and inactivates proteins, and regulates protein-protein interactions through the proteasome and lysosomes.DUB can reverse these effects by cleaving peptide or isopeptide bonds between ubiquitin and its substrate proteins. There are nearly 100 DUB genes in humans, which can be categorized into two main groups: cysteine proteases and metalloproteases. The cysteine proteases include ubiquitin-specific proteases (USP), ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCH), Machado-Josephin structural domain proteases (MJD), and ovarian tumor proteases (OTU). The metalloproteasome contains only Jab1/Mov34/Mpr1 Pad1 N terminal+ (MPN+) (JAMM) structural domain proteases.
Functions and Applications of Deubiquitinating Enzymes (DUBs)
Functions
The functions of deubiquitinating enzymes in the cell can be broadly categorized as follows:
1) They process ubiquitin precursors, producing free ubiquitin molecules.
2) They can remove ubiquitin chains from proteins, avoiding protein degradation by the proteasome and thus stabilizing proteins.
3) They can remove non-degradable ubiquitination signals attached to proteins.
4) They can ensure the homeostasis of ubiquitin molecules in the cell by preventing them from being degraded along with the substrate protein.
5) They can participate in the disassembly of free ubiquitin chains in the cell.
6) They can edit the type of ubiquitin chains by shearing them.
Applications
Due to the importance of deubiquitinating enzymes in regulating protein degradation and signaling pathways, they have become a hotspot in several fields. The following are some important applications of DUBs:
1) Drug discovery
DUBs have attracted widespread attention as potential drug targets. By interfering with the activity of deubiquitinating enzymes, they can regulate cell signaling pathways, inhibit tumorigenesis and development, and enhance immune response. Researchers are carrying out drug screening and design related to DUBs to find specific inhibitors and expect to use them in the treatment of cancer, inflammation, and other diseases.
2) Disease connections
Deubiquitinating enzymes play key roles in a variety of diseases. For example, aberrant deubiquitinating enzyme activity may lead to overstabilization or aberrant degradation of proteins, negatively affecting key processes such as gene expression, cell cycle regulation, and DNA repair. Therefore, DUBs have potential therapeutic and diagnostic value in the development and progression of diseases such as cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory diseases.
Available Resources of Deubiquitinating Enzymes (DUBs)
Creative BioMart is a leading provider of high-quality reagents and services for DUB research. They offer a comprehensive range of products including recombinant proteins, native proteins, cell & tissue lysates, transfected stable cell lines, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, antibodies, chromatography reagents, assay kits, and other products to facilitate DUB-related research.
In addition to products and customization services, Creative BioMart provides DUB-related signaling pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, DUB-related articles, articles, research areas, and other resources to support researchers studying DUB. Please visit the details page for specific available resources for each product. For more information, please contact our team.
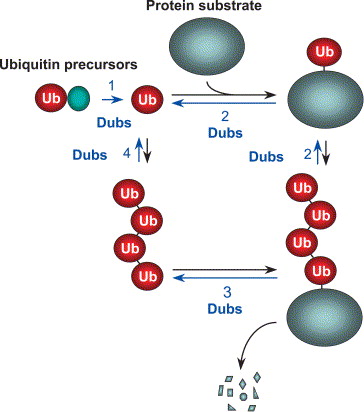 Fig. 1. Functions of DUBs in the ubiquitin pathway. Processing of ubiquitin precursors (1). Editing or rescue of ubiquitin conjugates, which are generally adducts to other proteins in the cell but can also be ligated to abundant small nucleophiles such as glutathione (2). Recycling of ubiquitin or ubiquitin oligomers from ubiquitin–protein conjugates targeted for degradation (3). Disassembly of unanchored ubiquitin oligomers (4). (Amerik AY, et al., 2004)
Fig. 1. Functions of DUBs in the ubiquitin pathway. Processing of ubiquitin precursors (1). Editing or rescue of ubiquitin conjugates, which are generally adducts to other proteins in the cell but can also be ligated to abundant small nucleophiles such as glutathione (2). Recycling of ubiquitin or ubiquitin oligomers from ubiquitin–protein conjugates targeted for degradation (3). Disassembly of unanchored ubiquitin oligomers (4). (Amerik AY, et al., 2004)
References:
- Li, Y; Reverter, D. Molecular Mechanisms of DUBs Regulation in Signaling and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 986.
- Amerik AY, Hochstrasser M. Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Nov 29;1695(1-3):189-207.

