IL-6 Family Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for IL-6 Family Receptors Research
Creative BioMart offers researchers a wide range of products related to IL-6 Family Receptors, including high-quality recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and others. Recognizing the unique requirements of each research project, we offer tailored services to ensure that our products meet your specific research goals.
In addition to our diverse product line, we are committed to providing a wealth of resources on the IL-6 family receptors. These resources cover a wide range of topics including pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, and research areas. As a knowledge center, these valuable resources enable researchers to deepen their understanding of IL-6 family receptors and their important role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF3R-8526H | Recombinant Human CSF3R protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| IL6ST-787H | Recombinant Human IL6ST protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CNTFR-3334H | Active Recombinant Human CNTFR protein, His-tagged | Human | Insect Cells | His |
| IL11RA-3155H | Recombinant Human IL11RA protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| Il11ra1-2294M | Recombinant Mouse Il11ra1, His tagged | Mouse | Human Cell | His |
| Il6ra-2297M | Recombinant Mouse Il6ra, His tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His |
| LEPR-800H | Recombinant Human LEPR, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| LIFR-611H | Active Recombinant Human LIFR protein (Met1-Ser833), His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | C-His |
| OSMR-2318H | Recombinant Human OSMR protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
About IL-6 Family Receptors
The IL-6 family of cytokines consists of several interleukins, including IL-6, IL-11, IL-27, IL-31, oncostatin M (OSM), ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), and others. These cytokines exert their effects by binding to specific receptors known as IL-6 family receptors.
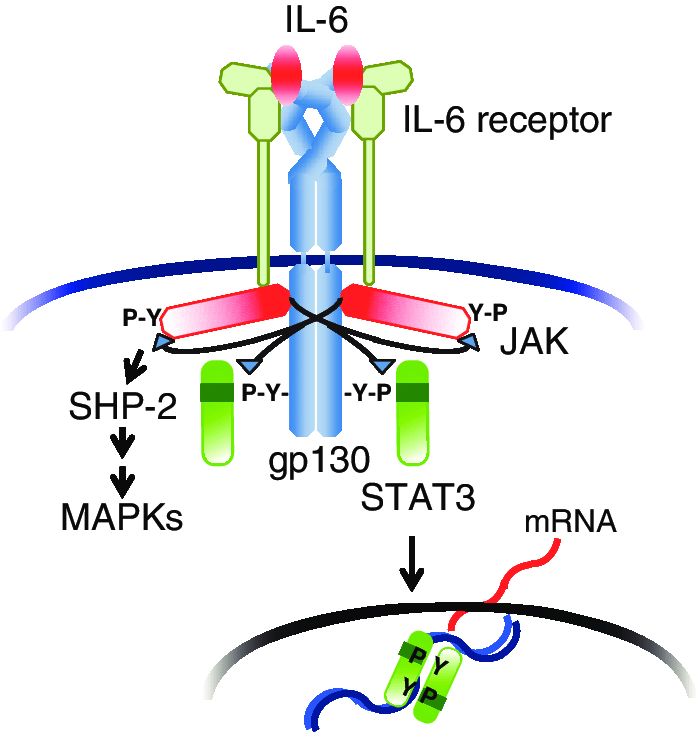 Fig.1 IL-6 receptor system. (Tanaka T, et al., 2013)
Fig.1 IL-6 receptor system. (Tanaka T, et al., 2013)
After binding of IL-6 to IL-6 receptor (IL-6R), the resultant IL-6/ IL-6R complex associates with gp130 and induces homodimerization of gp130; this in turn triggers activation of JAKs and tyrosine phosphorylation of gp130. The phosphorylated gp130 then recruits STAT3 via the SH2domain. Next, activated STAT3 translocates into the nucleus and regulates transcription for various sets of genes. Tyrosine-phosphorylated gp130 also recruits SHP-2 and activates the MAP kinase pathway.
IL-6 Receptor (IL-6R)
IL-6R is the primary receptor for IL-6. It exists in two forms: membrane-bound IL-6R (mIL-6R) and soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R). The mIL-6R is expressed on various immune cells, hepatocytes, and some other cell types. The sIL-6R is generated by proteolytic shedding of the extracellular domain of mIL-6R and can circulate in the blood. IL-6 binds to IL-6R, leading to the formation of a complex with a second receptor subunit called glycoprotein 130 (gp130).
Glycoprotein 130 (gp130)
gp130 is a common signaling receptor subunit shared by all IL-6 family cytokines. It is required for the activation of downstream signaling pathways. Upon IL-6 binding to the IL-6R, the IL-6/IL-6R complex associates with gp130, leading to the assembly of a hexameric receptor complex. This hexameric complex activates intracellular signaling cascades.
IL-11 Receptor (IL-11R)
IL-11R is the specific receptor for IL-11. It consists of at least two subunits: IL-11Rα and gp130. IL-11 binds to IL-11Rα, which then associates with gp130 to initiate downstream signaling events.
IL-27 Receptor (IL-27R)
IL-27R is a heterodimeric receptor composed of two subunits: IL-27Rα (also known as WSX-1 or TCCR) and gp130. IL-27 binds to IL-27Rα, leading to the recruitment of gp130 and subsequent activation of downstream signaling pathways.
Other Receptors
The remaining IL-6 family cytokines, such as IL-31, OSM, CNTF, CT-1, and LIF, also exert their effects by binding to specific receptor complexes. These receptors often involve a combination of gp130 and additional receptor subunits, such as IL-31 receptor α (IL-31RA), OSM receptor β (OSMRβ), CNTF receptor α (CNTFRα), LIF receptor β (LIFRβ), and others. The specific combinations of receptor subunits determine the signaling properties and cellular responses to these cytokines.
The activation of IL-6 family receptors triggers intracellular signaling pathways, including the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways. These pathways regulate a wide range of cellular processes, including immune responses, inflammation, hematopoiesis, cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.
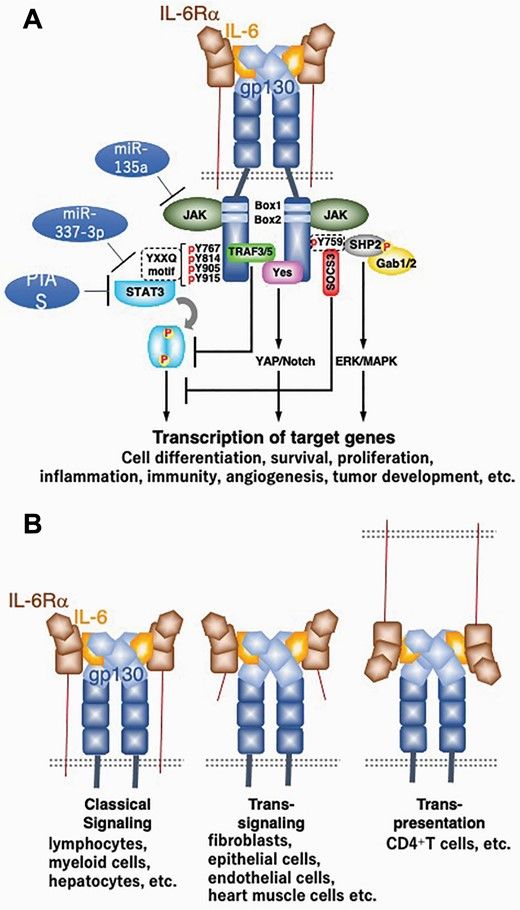 Fig.2 IL-6 receptor and signaling. (Toshio Hirano, 2021)
Fig.2 IL-6 receptor and signaling. (Toshio Hirano, 2021)
Role of IL-6 Family Receptors in Disease
IL-6 family receptors and their associated cytokines play significant roles in various diseases. Dysregulation of these receptors and their signaling pathways has been implicated in a range of conditions, including inflammatory, autoimmune, and neoplastic diseases.
Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases
IL-6 and IL-6R signaling have been implicated in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Overactive IL-6 signaling is associated with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis. Enhanced IL-6 receptor signaling contributes to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, activation of immune cells, and perpetuation of chronic inflammation.
Cytokine Storm Syndromes
Cytokine storm syndromes, characterized by excessive and dysregulated immune responses, involve aberrant IL-6 receptor signaling. For example, in severe cases of COVID-19, an overactive immune response leads to a cytokine storm, and IL-6 signaling plays a crucial role in the amplification of inflammation. IL-6 receptor blockade has been explored as a potential therapeutic approach in mitigating the cytokine storm and associated complications.
Cancer
IL-6 family receptors and their cytokines have been implicated in the development and progression of certain cancers. Elevated IL-6 signaling is associated with tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to treatments. Activation of IL-6 family receptors can promote tumor cell survival, proliferation, and invasion. Cancers such as multiple myeloma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and ovarian cancer show dysregulated IL-6 receptor signaling, making it a potential target for therapeutic interventions.
Hematological Disorders
IL-6 family receptors play a role in various hematological disorders. For instance, IL-6 signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma, a plasma cell neoplasm. IL-6 promotes the survival and proliferation of myeloma cells and contributes to bone destruction in the disease. Targeting IL-6 receptors has shown promise in inhibiting myeloma growth and bone resorption.
Metabolic Disorders
IL-6 family receptors are implicated in metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Elevated IL-6 levels and increased IL-6 receptor signaling have been observed in these conditions. IL-6 can contribute to insulin resistance, chronic low-grade inflammation, and adipose tissue dysfunction, all of which are associated with metabolic abnormalities.
Understanding the role of IL-6 family receptors in disease pathogenesis provides insights into potential therapeutic targets. Targeting these receptors or their downstream signaling pathways has shown promise in preclinical and clinical studies for the treatment of various diseases. However, it's important to consider the complex and context-dependent nature of IL-6 family receptor signaling in different diseases, as well as the potential side effects associated with modulating these pathways.
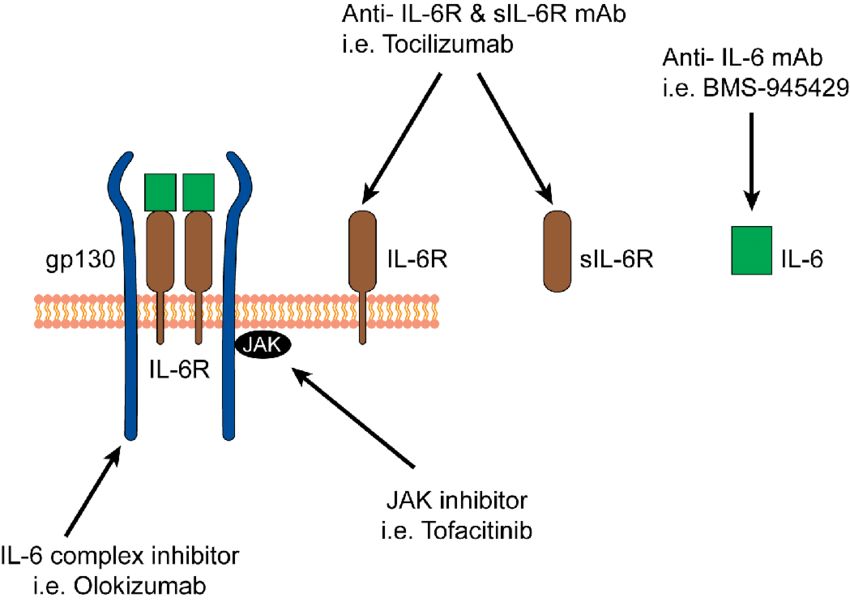 Fig.3 Therapeutic blockade of IL-6 and IL-6 receptor. (Liu X, et al., 2015)
Fig.3 Therapeutic blockade of IL-6 and IL-6 receptor. (Liu X, et al., 2015)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- Tanaka T, Ogata A, Narazaki M. Tocilizumab: An Updated Review of Its Use in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Application for Other Immune-Mediated Diseases. Clinical Medicine Insights: Therapeutics. 2013;5. doi:10.4137/CMT.S9282
- Toshio Hirano, IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer, International Immunology, Volume 33, Issue 3, March 2021, Pages 127–148
- Liu X, Teichtahl AJ, Wicks IP. Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis - from the laboratory to the bedside. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(17):2187-2197. doi:10.2174/1381612821666150310143332

