ROR1
-
Official Full Name
receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 -
Overview
ROR1 and ROR2 are orphan receptor tyrosine kinases that are most closely related to MuSK and the Trk family of neurotrophin receptors. They are characterized by the presence of extracellular frizzled-like cysteine-rich domains and membrane-proximal kringl -
Synonyms
ROR1;receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1;NTRKR1;tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1;neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor-related 1;neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor-related 1;dJ537F10.1;MGC99659
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Human / Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque
- Human/Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- Human Cells
- NS0
- Yeast
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- GST
- mFc
- Non
- Flag
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
Background
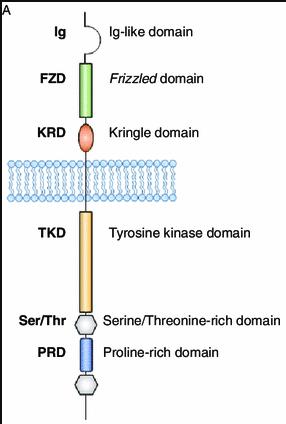
Fig1. ROR1 structure. (Nicholas Borcherding, 2014)
What is ROR1 protein?
ROR1 gene (receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p31. This gene encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor that modulates neurite growth in the central nervous system. The encoded protein is a glycosylated type I membrane protein that belongs to the ROR subfamily of cell surface receptors. It is a pseudokinase that lacks catalytic activity and may interact with the non-canonical Wnt signalling pathway. This gene is highly expressed during early embryonic development but expressed at very low levels in adult tissues. The ROR1 protein is consisted of 937 amino acids and ROR1 molecular weight is approximately 104.3 kDa.
What is the function of ROR1 protein?
ROR1 is a cell surface protein that is expressed in a variety of tumors. ROR1 plays an important role in embryonic and fetal development, but expression levels in adult tissues are usually low. Overexpression of ROR1 is closely related to the proliferation, survival and migration of cancer cells, and it promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating several signaling pathways, including the PI3K-AKT pathway. High expression of ROR1 is closely associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients.
ROR1 related signaling pathway
ROR1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating several signaling pathways, including the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. In non-small cell lung cancer cells, ROR1 can enhance the anti-apoptotic ability of tumor cells through interaction with MET and enhance EGF-induced signaling through interaction with EGFR. In addition, ROR1 also binds to Wnt5a to activate the atypical Wnt signaling pathway, thereby affecting the migration and invasion of tumor cells. In breast cancer cells, high expression of ROR1 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis, and it activates the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway through its interaction with Wnt5a, promoting the proliferation and migration of tumor cells.
ROR1 related diseases
ROR1 is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is overexpressed in several types of cancer, including breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and lung adenocarcinoma. It is also involved in the development of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, ROR1 has been linked to cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders like obesity and type 2 diabetes. In cancer, ROR1 plays a role in promoting tumor growth and survival, making it an attractive target for therapeutic interventions. In autoimmune diseases, ROR1 may contribute to the activation and proliferation of immune cells, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
Bioapplications of ROR1
Recombinant human ROR1 protein has potential bioapplications in various fields, including cancer biomarker detection, targeted therapy development, improved drug delivery systems, cellular signaling research, and potentially modulating immune responses in autoimmune diseases. Additionally, it might be useful in tissue engineering, cardiovascular and metabolic disorder research, diagnostic imaging, and vaccine development. These applications underscore rhROR1's dual role as a valuable tool for biological research and a promising target for therapeutic interventions.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Tomohiro Ishikawa, 2023
Ror1 is important for cancer growth and spread, and it's more common in cancer stem cells, but how it's controlled is not well known. In aggressive brain cancers like glioblastoma, Ror1 and Wnt5a are highly expressed and linked to worse survival. Ror1 levels rise in glioblastoma cells in spheroid culture, a change related to active Notch and hypoxia pathways. Inhibiting these pathways or expressing the Notch intracellular domain can regulate Ror1. Wnt5a binding to Ror1, influenced by these pathways, might help cancer cells form spheroids.
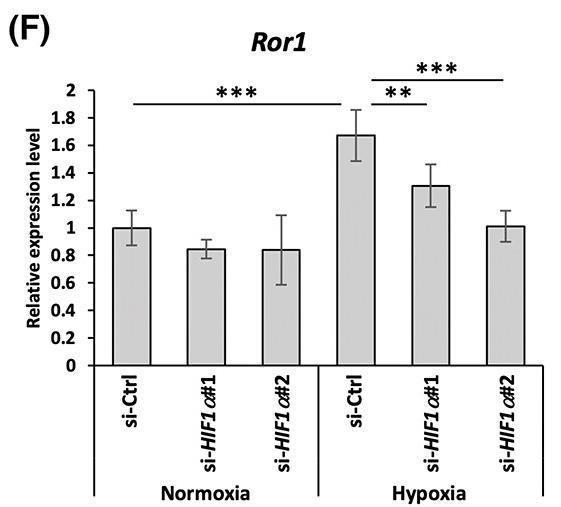
Fig1. mRNA levels of Ror1 were determined by qRT-PCR.
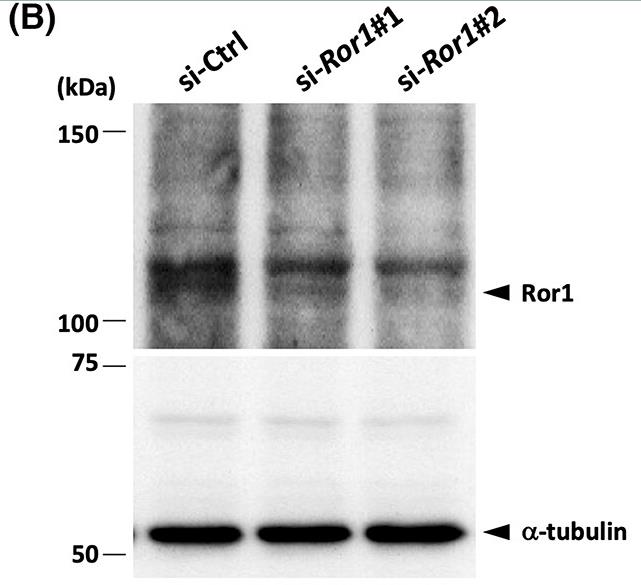
Fig2. Western blotting with the anti-Ror1 mAb.
Case Study 2: Flávia Arandas de Sousa, 2024
Flow cytometry-based immunophenotyping is crucial for diagnosing and classifying leukemias and lymphomas. While ROR1's role in chronic B lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is well documented, its expression in other mature B lymphoid neoplasms (MBLN) is less studied. In a study of 767 cases with suspected MBLN, researchers analyzed ROR1 expression and its correlation with other key markers. ROR1 was mainly found in CD5+/CD10- neoplasms, with 60.1% of cases showing positive expression. Notably, the CD5+/CD10- group had a notably higher rate (89.9%) and stronger ROR1 expression than other groups.
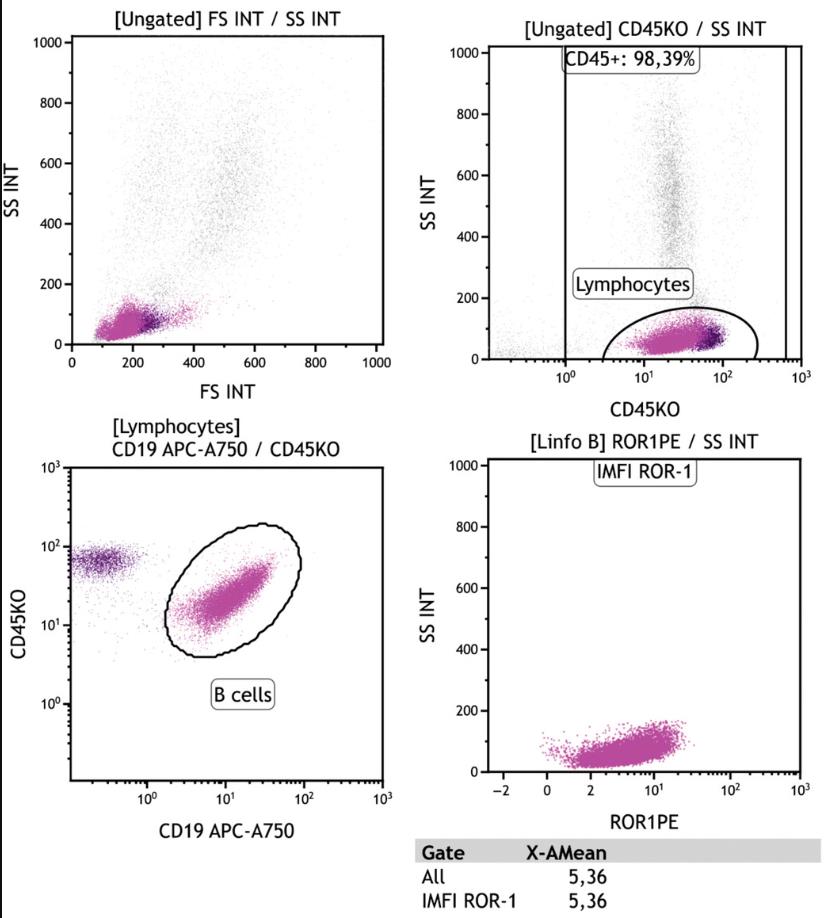
Fig3. Representative sample ROR1 positive.
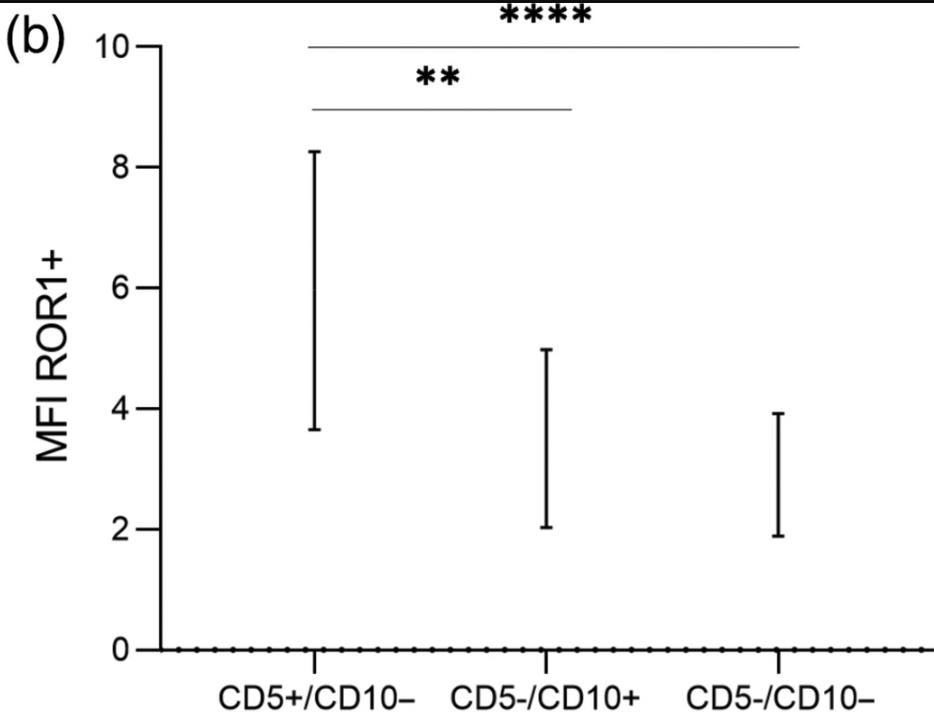
Fig4. Median MFI values of positive ROR1 expression and their interquartile range in CD5+/CD10−, CD5−/CD10− and CD5−/CD10+ neoplasms.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ROR1-051H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ROR1-1812H)
Involved Pathway
ROR1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ROR1 participated on our site, such as Beta-catenin independent WNT signaling,Nuclear Receptors,PCP/CE pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ROR1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Signaling by Wnt | ASH2L,RSPO1,SOX7,FMNL3,LGR5,SOX4A,TNKS2,RYK,SOX13,ROR2 |
| PCP/CE pathway | ROR2,PRICKLE1B,PRICKLE1,RYK |
| Signal Transduction | MDKA,HHAT,ARHGAP31,KLHL12,TAGAPA,PYY,CRHR2,ARAP1,PDE10A,RHOT1A |
| WNT5A-dependent internalization of FZD2, FZD5 and ROR2 | ROR2 |
| Nuclear Receptors | NR2F6,VDRB,NR2E1,RORAA,NR2F1A,NR2F2,NR2F1,NR1I3,NR0B1,NR1D2 |
| Beta-catenin independent WNT signaling | CLTB,ROR2,MOV10,ITPR2,AP2M1,AP2B1,PRICKLE1,RYK,CLTC,CTNNB2 |
Protein Function
ROR1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,Wnt-protein binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ROR1 itself. We selected most functions ROR1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ROR1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Wnt-protein binding | FZD9,FZD7B,FZD6,FZD8A,LRP2A,FZD3A,FZD7,FZD8B,FRZB,FZD9B |
| ATP binding | CAMK2D1,PRPF4B,KIF2B,HSPA7,NARS2,ATP2B2,PFAS,DNAJA4,AK5L,SMC2 |
| protein binding | FKBP1A,ARHGAP26,ZNF625,FAT4,LIN9,PDGFRA,EXOC4,MEPE,LMO2,ABI2 |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | CADM2B,EGFR,INSRR,RET,MUSK,TRIM27,KITB,EPHA4B,KIT,NPTNB |
Interacting Protein
ROR1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ROR1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ROR1.
SRC;Src;EGFR
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zhang, SP; Cui, B; et al. Ovarian cancer stem cells express ROR1, which can be targeted for anti-cancer-stem-cell therapy. PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 111:17266-17271(2014).
- Hojjat-Farsangi, M; Moshfegh, A; et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1-An oncofetal antigen for targeted cancer therapy. SEMINARS IN CANCER BIOLOGY 29:21-31(2014).



