Efna1
-
Official Full Name
ephrin-A1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the ephrin (EPH) family. The ephrins and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, especially in the nervous system -
Synonyms
EFNA1;ephrin-A1;EPLG1, TNFAIP4;ECKLG;LERK1;TNF alpha-induced protein 4;ligand of eph-related kinase 1;immediate early response protein B61;eph-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 1;tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 4;tumor necrosis;B61;EFL1;EPLG1;LERK-1;TNFAIP4
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Human
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- HeLa
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- GST
Background
What is EFNA1 protein?
EFNA1 (ephrin A1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q22. This gene encodes a member of the ephrin (EPH) family called EFNA1, also known as Ephrin A1 (EphA1), a member of the ephrin (EPH) family. The ephrins and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, especially in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage. Human Ephrin A1 binds to the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2, EphA4, EphA5, EphA6 and EphA7. Also binds with low affinity to EphA1. The EFNA1 protein is consisted of 205 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 23.8 kDa.
What is the function of EFNA1 protein?
Ephrin-A1 plays an important role in the development of ephrin-A1, regulating axonal guidance, synaptic formation and nerve cell migration. In adult tissues, Ephrin-A1 also plays a key role in processes such as nervous system maintenance and repair, angiogenesis, immune system and cancer development. In addition, Ephrin-A1 can also interact with other signaling pathways and influence cellular behavior. For example, interactions with the Wnt signaling pathway can influence cell fate decisions and embryonic development. Interaction with the TGF-β signaling pathway can regulate cell migration and epithelial mesenchymal transformation.
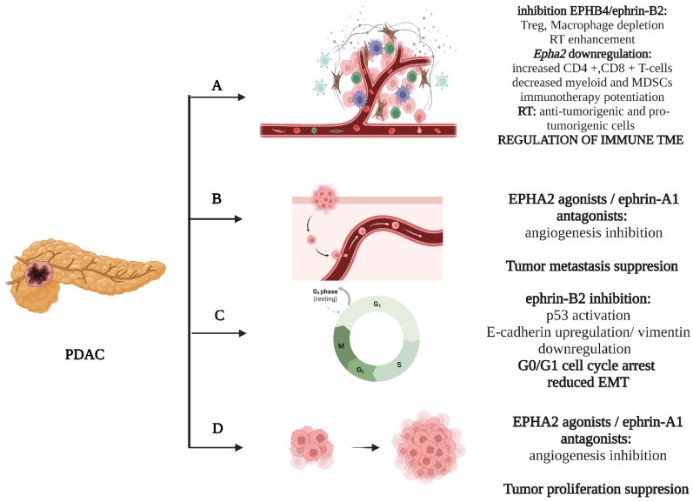
Fig1. (D) EPHA2/ephrin-A1 induce tumor growth. (Stavros P Papadakos, 2023)
EFNA1 Related Signaling Pathway
After binding to Eph receptor, Ephrin-A1 could trigger downstream signal transduction pathways including MAPK, PI3K/AKT and Rho family GTPase signaling pathways, which were involved in multiple biological processes such as cell proliferation, migration, adhesion, differentiation and apoptosis. When Ephrin-A1 protein activated EphA receptor, tyrosine kinase activity in EphrA receptor was inhibited, mediating the change of cell attachment and growth anchoring.
EFNA1 Related Diseases
Several studies have suggested that abnormal expression of Ephrin-A1 is associated with the development and metastasis of tumors like breast cancer and gastric cancer. In addition, Ephrin-A1 has been found to play an important role in neurological diseases like glioblastoma, cardiovascular diseases and inflammatory diseases.
Bioapplications of EFNA1
Ephrin-A1 plays an important role in tumorigenesis and development, and several antibodies and small molecule inhibitors targeting Eph receptors are currently in preclinical or clinical trials.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Pitna Kim, 2019
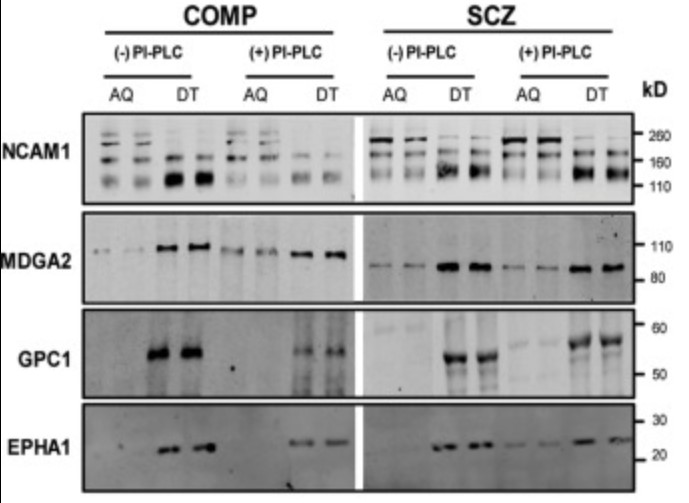
Fig1. PI-PLC sensitivity of membrane-associated GPI-APs in schizophrenia.
Case Study 2: Yi Wang, 2016
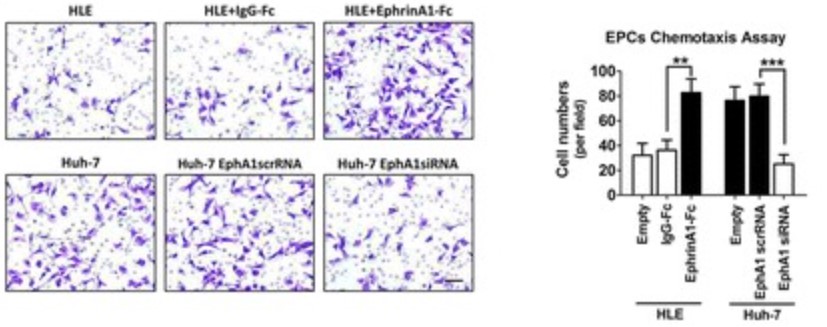
Fig2. Boyden chamber staining of EPCs' chemotaxis to HCC cells with different EphA1 levels, Asterisks indicate significant differences (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) with respect to the corresponding control.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (EFNA1-3096H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
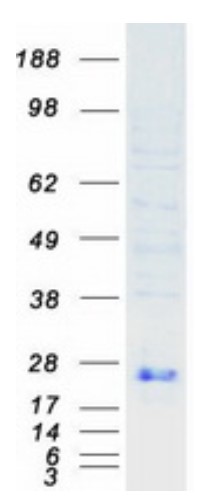
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (EFNA1-1561H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
Efna1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Efna1 participated on our site, such as Arf6 signaling events,Axon guidance,Developmental Biology, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Efna1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| EPHA-mediated growth cone collapse | EFNA5,EPHA4A,EFNA2,EFNA2A,KDR,SHB,EFNA3B,EPHA2A,EFNA1A,MYL12B |
| Developmental Biology | CSNK2A2,PITPNA,CSNK2B,UNC5D,DOCK1,EFNA2,CACNG3,MED20,NRG4,EFNB1 |
| Axon guidance | NRG3,ARPC5,NRAS,MAPK1,DPYSL5,CDK5R1B,GPC1A,ARPC2,PAK7,AP2S1 |
| EPHA forward signaling | EFNA5,ARHGEF15,BLK,CRKL,EFNA2,EFNA3,EPHA2 |
| EPH-Ephrin signaling | ARPC3,EPHA2,AP2S1,AP2M1,ARPC5,EPHA4A,EFNA3B,ARHGEF28,CFL1,EFNB3 |
| EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells | EFNB2,EFNA1A,EFNB1,EFNA2A,EFNA5,EFNB3,EPHA10,EFNA2,AP2S1,CLTB |
| Arf6 signaling events | EGF,ADAP1,ADRB2,USP6,EGFR,KIF13B,GULP1,ARAP2,FBXO8,IPCEF1 |
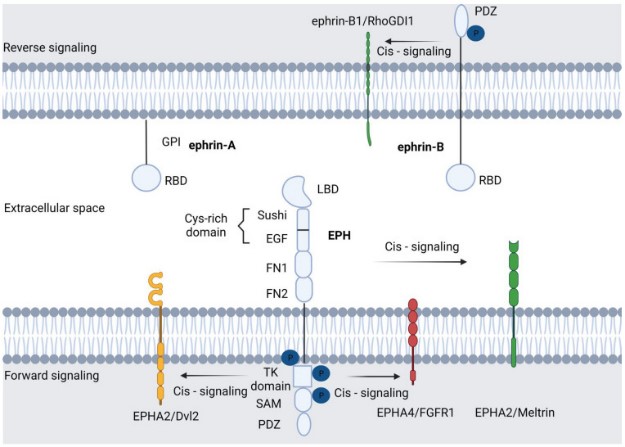
Fig2. Basic molecular structure of the EPH/ephrin signaling compartment. In the plasma membrane, ephrin-A ligands are hooked by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor, although they can also activate distant EPH receptors. (Stavros P Papadakos, 2023)
Protein Function
Efna1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ephrin receptor binding,protein binding,receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Efna1 itself. We selected most functions Efna1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Efna1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor binding | CD86,PLAT,GRIN2A,NPPC,SMARCD1,SERPINE2,TENC1,FGF13B,LRRC4B,C1QTNF2 |
| protein binding | LINC00482,NKX2,SLA,CLPP,NEK2,NCOR2,RHOV,FOXO3B,PALM,ZNF488 |
| ephrin receptor binding | GRB2,EFNB2,ANKS1B,EFNA1A,Anks1,CBL,PIK3CG,NTRK1,EFNB1,EFNA4 |
Interacting Protein
Efna1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Efna1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Efna1.
EPHA2;PPBP;XRCC6;EEF1G;SUMO2;KAT5
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Miao, H; Gale, NW; et al. EphA2 promotes infiltrative invasion of glioma stem cells in vivo through cross-talk with Akt and regulates stem cell properties. ONCOGENE 34:558-567(2015).
- McKinney, N; Yuan, LP; et al. EphrinB1 expression is dysregulated and promotes oncogenic signaling in medulloblastoma. JOURNAL OF NEURO-ONCOLOGY 121:109-118(2015).




