MUC1
-
Official Full Name
mucin 1, cell surface associated -
Overview
This gene encodes a membrane-bound protein that is a member of the mucin family. Mucins are O-glycosylated proteins that play an essential role in forming protective mucous barriers on epithelial surfaces. These proteins also play a role in intracellular signaling. This protein is expressed on the apical surface of epithelial cells that line the mucosal surfaces of many different tissues including lung, breast stomach and pancreas. This protein is proteolytically cleaved into alpha and beta subunits that form a heterodimeric complex. The N-terminal alpha subunit functions in cell-adhesion and the C-terminal beta subunit is involved in cell signaling. Overexpression, aberrant intracellular localization, and changes in glycosylation of this protein have been associated with carcinomas. This gene is known to contain a highly polymorphic variable number tandem repeats (VNTR) domain. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011] -
Synonyms
MUC1;mucin 1, cell surface associated;EMA;MCD;PEM;PUM;KL-6;MAM6;MCKD;PEMT;CD227;H23AG;MCKD1;MUC-1;ADMCKD;ADMCKD1;CA 15-3;MUC-1/X;MUC1/ZD;MUC-1/SEC;mucin-1;episialin;DF3 antigen;H23 antigen;cancer antigen 15-3;krebs von den Lungen-6;mucin 1, transmembrane;carcinoma-associated mucin;polymorphic epithelial mucin;peanut-reactive urinary mucin;tumor associated epithelial mucin;breast carcinoma-associated antigen DF3;tumor-associated epithelial membrane antigen
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Cattle
- Bovine
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Human
- Mouse
- Human Ascites Fluid
- C-hFc
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Bovine Submaxillary Gland
- Yeast
- Wheat Germ
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- His
- LEVLFQ
- Non
- S
- mFc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
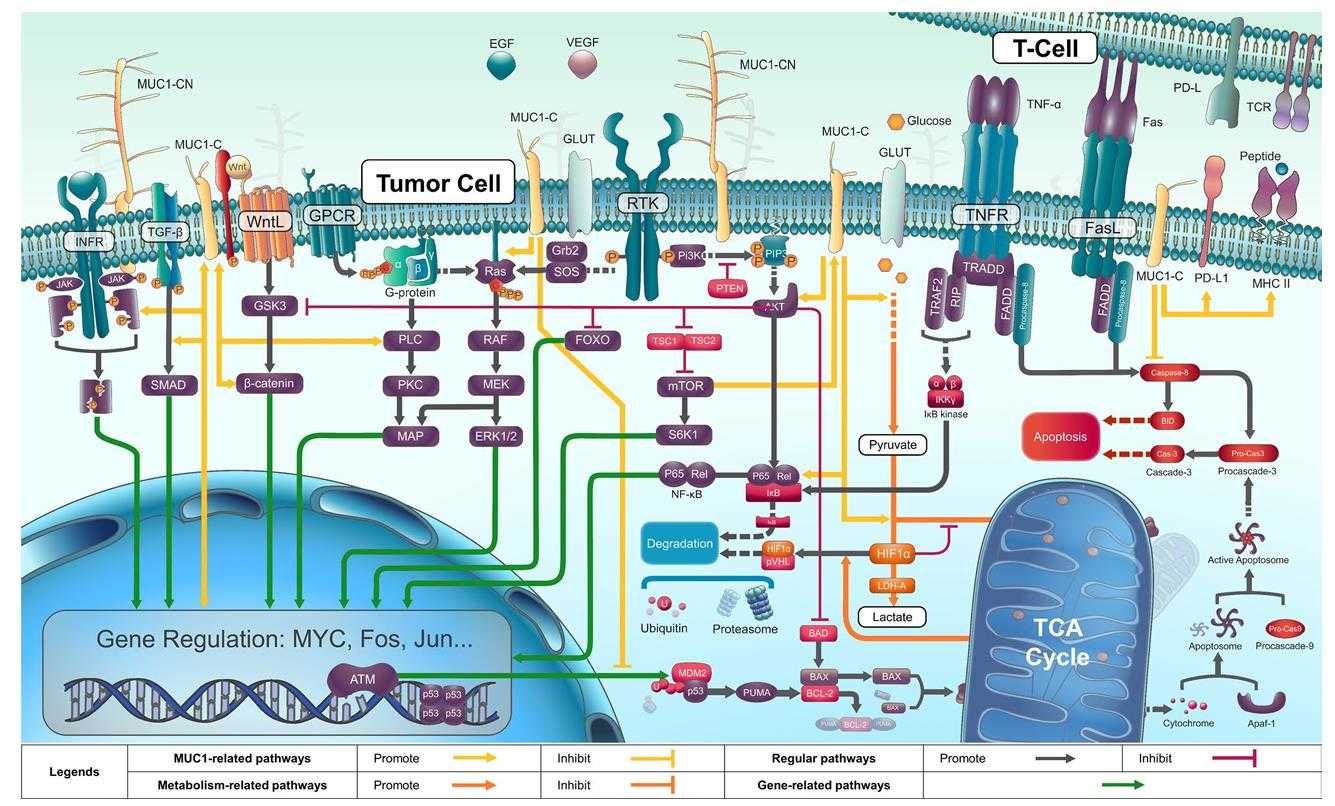
Fig1. A glance at the functions of MUC1: related cell pathways and molecules. (Weiqiu Jin, 2023)
What is MUC1 Protein?
MUC1 gene (mucin 1, cell surface associated) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q22. This gene encodes a membrane-bound protein that is a member of the mucin family. Mucins are O-glycosylated proteins that play an essential role in forming protective mucous barriers on epithelial surfaces. These proteins also play a role in intracellular signaling. This protein is expressed on the apical surface of epithelial cells that line the mucosal surfaces of many different tissues including lung, breast stomach and pancreas. This protein is proteolytically cleaved into alpha and beta subunits that form a heterodimeric complex. The N-terminal alpha subunit functions in cell-adhesion and the C-terminal beta subunit is involved in cell signaling. The MUC1 protein is consisted of 1255 amino acids and MUC1 molecular weight is approximately 122.1 kDa.
What is the Function of MUC1 Protein?
In normal cells, MUC1 acts as a lubricant, humectant, and physical barrier through its structure and biochemical properties, protecting cells from extreme environments. However, in cancer cells, MUC1 often undergoes abnormal glycosylation and overexpression, and is involved in cancer invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and apoptosis, which is achieved through its participation in intracellular signaling processes and the regulation of related biomolecules. The function of MUC1 protein involves several signaling pathways, including PI3K/AKT, RTK, HIF-1, NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin and MAPK, and plays a regulatory role in tumors.
MUC1 Related Signaling Pathway
The multiple functions of MUC1 protein in tumor development have been extensively studied, and it is involved in a variety of signaling pathways related to tumor proliferation, invasion and metastasis, and chemotherapy resistance. MUC1 consists of a nitrogen-terminus subunit (MUC1-N) and a carbon-terminus subunit (MUC1-C), which form a heterodimer on the cell membrane by non-covalent bonding. In addition, the cytoplasmic domain of MUC1-C contains multiple tyrosine, serine, and threonine residues, which are potential phosphorylation sites for a variety of kinases and can regulate a variety of intracellular signaling pathways. MUC1-C interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor family and other tyrosine kinase receptors, and is involved in signaling pathways including PI3K/AKT, MAP, NF-κB, Wnt, STAT, P53, and Erα. These signaling pathways play an important role in the survival, proliferation and migration of cancer cells.
MUC1 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression and glycosylation changes of MUC1 protein play a central role in malignant tumors of various epithelial cell origins, especially in breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, which significantly affect disease progression and patient prognosis by promoting tumor cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis and enhancing the immune escape ability of the tumor microenvironment. In addition, specific forms of MUC1 serve as biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment in some cancers, and its high expression on the surface of tumor cells also makes it a potential target for immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
Bioapplications of MUC1
As a potential target for tumor therapy and diagnosis, the off-the-shelf application of MUC1 is mainly focused on the development of immunotherapies against MUC1, including monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, antibody drug conjugators (ADCs), bisspecific antibodies, CAR-T and CAR-NK cell therapies. These therapies take advantage of the high expression of MUC1 on the surface of tumor cells to inhibit tumor growth through specific binding, promote immune response, or directly deliver drugs to tumor cells, and some of these therapies have entered clinical trials, showing potential for treating a variety of epithelial tumors. In addition, abnormal expression of MUC1 also makes it an important biomarker for early detection and prognosis assessment of cancer.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ayako Nakashoji, 2024
The MUC1-C protein is aberrantly expressed in adenocarcinomas of epithelial barrier tissues and contributes to their progression. Less is known about involvement of MUC1-C in the pathogenesis of squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). Here, the MUC1 gene is upregulated in advanced head and neck SCCs (HNSCC). Studies of HNSCC cell lines demonstrate that the MUC1-C subunit regulates expression of (i) RIG-I and MDA5 pattern recognition receptors, (ii) STAT1 and IFN regulatory factors, and (iii) downstream IFN-stimulated genes. MUC1-C integrates chronic activation of the STAT1 inflammatory pathway with induction of the ∆Np63 and SOX2 genes that are aberrantly expressed in HNSCCs. In extending those dependencies, MUC1-C is necessary for NOTCH3 expression, self-renewal capacity, and tumorigenicity.
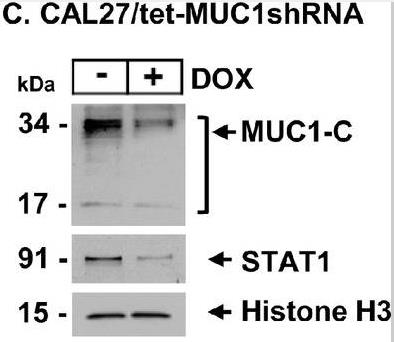
Fig1. Purified chromatin from CAL27/tet-MUC1shRNA cells was immunoblotted.
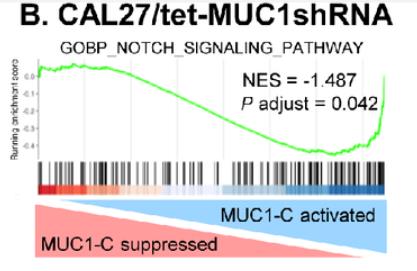
Fig2. GSEA of RNA-seq data from CAL27/tet-MUC1shRNA cells.
Case Study 2: Yoshihiro Morimoto, 2023
Aberrant expression of MUC1-C in cancers has been linked to depletion and dysfunction of T cells in the tumor microenvironment. In contrast, there is no known involvement of MUC1-C in the regulation of natural killer (NK) cell function. Targeting MUC1-C genetically and pharmacologically in cancer cells was performed to assess effects on intracellular and cell surface expression of the MHC class I chain-related polypeptide A (MICA) and MICB ligands. MUC1-C interactions with ERp5 and RAB27A were assessed by coimmunoprecipitation and direct binding studies. The studies demonstrate that MUC1-C represses expression of the MICA and MICB ligands that activate the NK group 2D receptor. Targeting MUC1-C genetically and pharmacologically with the GO-203 inhibitor induced intracellular and cell surface MICA/B expression but not MICA/B cleavage. Mechanistically, MUC1-C regulates the ERp5 thiol oxidoreductase that is necessary for MICA/B protease digestion and shedding. In addition, MUC1-C interacts with the RAB27A protein, which is required for exosome formation and secretion.
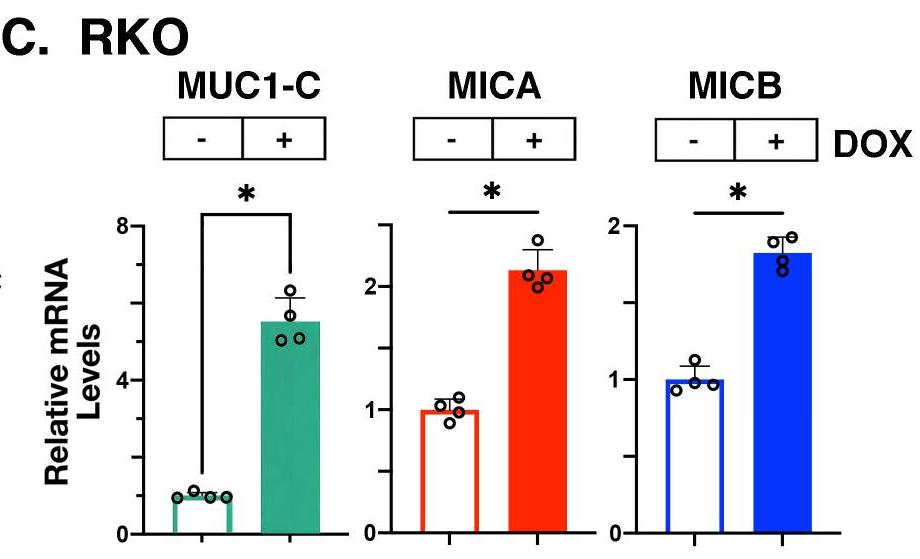
Fig3. RKO cells were analyzed for MUC1-C(AQA), MICA and MICB mRNA levels.
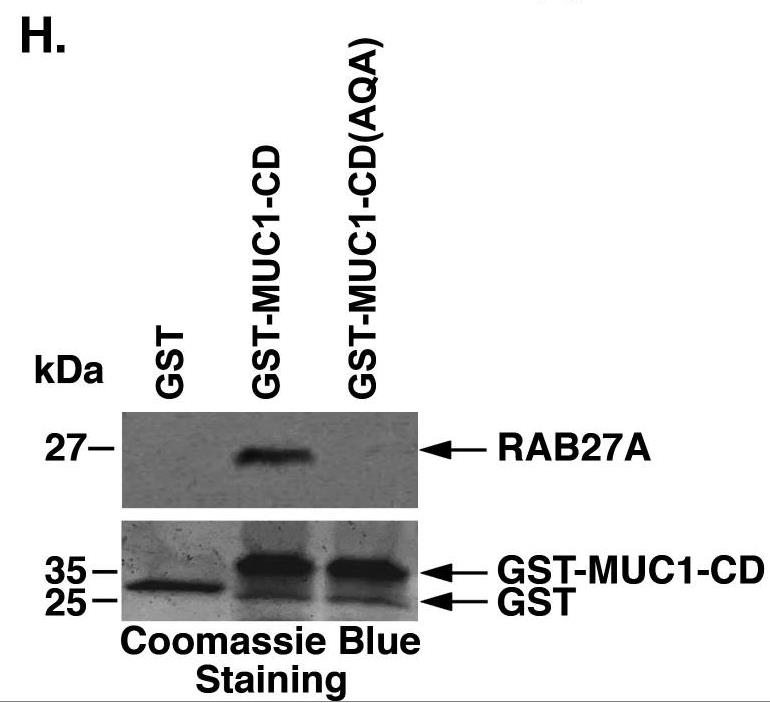
Fig4. GST, GST-MUC1-CD and GST-MUC1-CD(AQA) were incubated with purified RAB27A.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MUC1-051H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MUC1-244H)
Involved Pathway
MUC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MUC1 participated on our site, such as IL-7 Signaling Pathway,Metabolism of proteins,O-linked glycosylation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MUC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | IL4,CD3E,PAK2,CD247,NFKBIE,MAPK13,PDCD1,DLG1,MAP2K1,PPP3R2 |
| Termination of O-glycan biosynthesis | MUC5AC,MUC21,MUC13,MUC20,MUCL1,MUC4,MUC15,MUC12 |
| O-linked glycosylation | SPON1A,MUC4,ADAMTS18,ADAMTS5,ADAMTS10,ADAMTSL1,MUC13,ADAMTSL4,GALNTL5,SPON1B |
| IL-7 Signaling Pathway | STAM2,IRF1B |
| O-linked glycosylation of mucins | MUC5AC,ST6GALNAC2,KCNA6,MUC4,A4GNT,MUCL1,MUC15,GALNT13,MUC21,B3GNT8 |
| Post-translational protein modification | CNIH,EIF5A2,PIGK,NSMCE2,SENP5,TRAPPC2,SMC6,CNIH3,MAGT1,PHC2 |
| Metabolism of proteins | HSCB,IGFBP5A,KLK13,DDIT3,TGFBI,CTSH,ZDHHC2,PCSK1,MBOAT4,NSMCE4A |
Protein Function
MUC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MUC1 itself. We selected most functions MUC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MUC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
MUC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MUC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MUC1.
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zhan, XX; Zhao, B; et al. Expression of MUC1 and CD176 (Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen) in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas. ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY 26:21-26(2015).
- Zhang, Q; Wang, F; et al. Dual-color labeled anti-mucin 1 antibody for imaging of ovarian cancer: A preliminary animal study. ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9:1231-1235(2015).




