Th1 Cells
Related Symbol Search List
- CXCR3
- CD4
- Ifng
- TNFB
- TNFa
- CCR5
- CD3e
- IL-10
- IL18R1
- IL2
- TBX21
- CD3G
- IFNGR1
- IL6ST
- CCR1
- IFNLR1
- IL12RB1
- IL12RB2
- IL18
- IL19
- IL27
- STAT1
- STAT4
Immunology Background
Available Resources Related to Th1 Cells
Creative BioMart is dedicated to advancing Th1 cell research by providing high-quality products, tailored services, and valuable resources to support scientific discovery and advancement in Th1 cell biology and related fields.
| We offer a wide selection of high-quality products specifically designed for Th1 cell research, these include recombinant proteins, GMP proteins, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, antibodies, and small molecules targeting key Th1 cell markers, cytokines, and signaling pathways. | |
| We understand the unique needs of Th1 cell researchers and offer customizable services to meet specific research requirements, such as custom protein production, custom antibody development, and gene expression analysis. | |
| We also provide valuable resources to support Th1 cell research, such as technical support, protocols and literature, and data analysis tools. Even more critical is our collection of resources for analyzing and interpreting Th1 cell-related data, including protein functions, protein interactions, involved pathways, and other valuable information. |
About Th1 Cells
Th1 cells are a subset of CD4+ T helper cells that play a crucial role in cellular immune responses against intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and certain bacteria. They are characterized by their ability to produce specific cytokines and orchestrate immune responses aimed at eliminating infected cells. Th1 cells are essential for effective host defense and immune regulation. Here is an introduction to Th1 cells, including their function, differentiation, and regulatory mechanisms:
Function of Th1 Cells
- Cell-Mediated Immunity: Th1 cells are primarily involved in cell-mediated immune responses. They secrete cytokines such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-2 (IL-2). These cytokines activate macrophages, enhance phagocytosis, and promote the killing of intracellular pathogens. Th1 cells also stimulate the production of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), which directly kill infected cells.
- Inflammation Regulation: Th1 cells regulate the inflammatory response by promoting the recruitment and activation of immune cells, including macrophages and neutrophils. They also contribute to the formation of granulomas, which are organized structures that contain infected cells and limit the spread of pathogens.
- Autoimmunity: Dysregulation of Th1 cells can lead to autoimmunity. Excessive Th1 cell activation and cytokine production can result in chronic inflammation and tissue damage, contributing to autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Differentiation of Th1 Cells
The differentiation of Th1 cells is influenced by various factors:
- Antigen Presentation: Dendritic cells, macrophages, and other antigen-presenting cells (APCs) capture and process antigens derived from intracellular pathogens. They present these antigens to naïve CD4+ T cells through major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules, triggering T cell activation.
- Cytokine Signals: Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a key cytokine involved in Th1 cell differentiation. IL-12 stimulates the expression of the transcription factor T-bet (T-box expressed in T cells), which is crucial for Th1 cell commitment. T-bet promotes the production of IFN-γ and other Th1-associated cytokines.
Regulatory Mechanisms
Several regulatory mechanisms control Th1 cell differentiation, maintenance, and function:
- Transcription Factors: T-bet is the master regulator of Th1 cell differentiation. It promotes the expression of genes associated with Th1 cell function, including cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α) and chemokine receptors (CXCR3). Transcriptional repressors, such as GATA-3 and STAT6, inhibit the differentiation of Th1 cells to maintain lineage stability.
- Cytokine Cross-Talk: Various cytokines influence Th1 cell development and function. IL-12, produced by APCs, is crucial for Th1 cell differentiation. IFN-γ, an autocrine cytokine produced by Th1 cells, reinforces their commitment and enhances their effector functions.
- Negative Regulation: Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a role in suppressing Th1 cell responses to prevent excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. Tregs produce anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), which inhibit Th1 cell activation and cytokine production.
Understanding the regulation and function of Th1 cells is essential for devising strategies to modulate immune responses in various diseases. Manipulating Th1 cell activity may have therapeutic implications for enhancing immune responses against intracellular pathogens or dampening autoimmune responses. Further research is needed to uncover the intricate mechanisms underlying Th1 cell biology and their potential applications in immunotherapy.
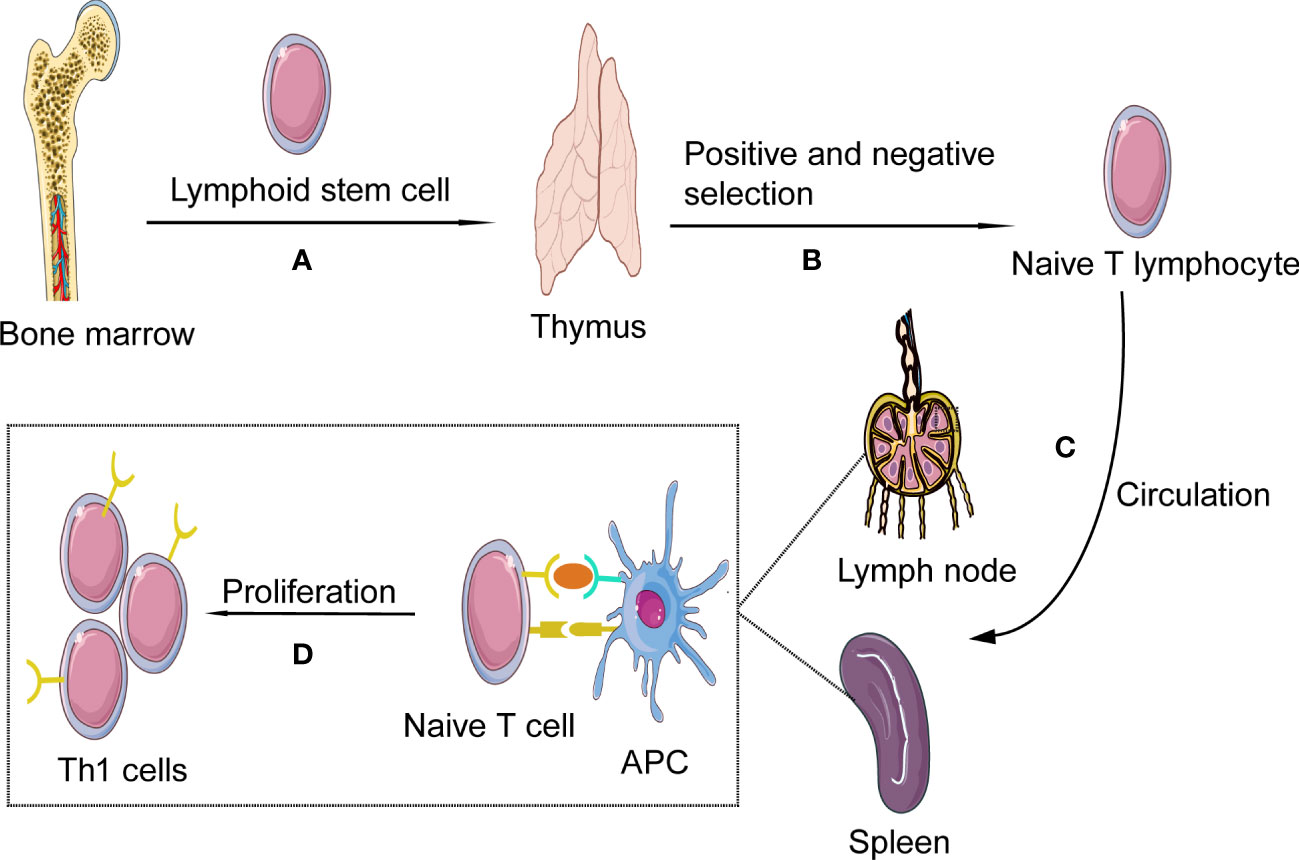 Fig.1 Th1 cells formation and activation. (Chen J, et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Th1 cells formation and activation. (Chen J, et al., 2023)
Key Molecules Involved in the Function of Th1 Cells
Th1 cells exert their functions through the production of specific cytokines and the expression of key molecules on their cell surface. These molecules play crucial roles in mediating immune responses and regulating the activity of Th1 cells. Here are some key molecules involved in the function of Th1 cells:
| Key molecules type | Functions |
|---|---|
| Interferon-Gamma (IFN-γ) | IFN-γ is the hallmark cytokine produced by Th1 cells. It plays a central role in cell-mediated immune responses against intracellular pathogens. IFN-γ activates macrophages, enhances phagocytosis, and promotes the killing of infected cells. It also upregulates antigen presentation by increasing the expression of MHC class I and II molecules on infected cells. |
| T-bet | T-bet is a transcription factor that is critical for Th1 cell differentiation and function. It is induced by IL-12 signaling and acts as a master regulator of Th1 cell lineage commitment. T-bet promotes the expression of genes involved in Th1 cell effector functions, including IFN-γ. It also represses the expression of genes associated with other T cell lineages. |
| IL-12 Receptor (IL-12R) | Th1 cells express the IL-12 receptor, which consists of two subunits: IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ2. IL-12Rβ2 is specific to Th1 cells and is required for IL-12 signaling. Engagement of IL-12 with its receptor activates STAT4 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 4) signaling pathway, leading to T-bet induction and Th1 cell differentiation. |
| CD40 Ligand (CD40L) | CD40L is expressed on the surface of activated Th1 cells. It interacts with CD40, which is expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells and macrophages. This interaction provides a co-stimulatory signal to APCs, enhancing their antigen-presenting function and promoting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-12. |
| Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 | Th1 cells express the chemokine receptor CXCR3, which binds to chemokines such as CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11. CXCR3 mediates the migration of Th1 cells to inflamed tissues, where they can exert their effector functions. It plays a crucial role in the recruitment of Th1 cells to sites of infection or inflammation. |
| CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen-4) | CTLA-4 is a co-inhibitory molecule expressed on activated Th1 cells. It competes with the co-stimulatory molecule CD28 for binding to B7 molecules on APCs, leading to downregulation of T cell activation. CTLA-4 dampens the immune response by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting the development of regulatory T cells. |
| IL-18 Receptor (IL-18R) | IL-18R is expressed on Th1 cells and is involved in their activation and cytokine production. IL-18, together with IL-12, can enhance IFN-γ production by Th1 cells, reinforcing their effector functions. |
These molecules collectively contribute to the functions of Th1 cells by regulating their differentiation, cytokine production, migration, interaction with APCs, and immune regulation. Understanding the roles and interactions of these key molecules is crucial for deciphering the mechanisms underlying Th1 cell-mediated immune responses and developing targeted interventions in various diseases.
The Role of Th1 Cells and Related Molecules in Various Diseases
Th1 cell-related molecules play critical roles in various diseases, contributing to their pathogenesis and progression. Here, we'll explore the involvement of these molecules in different disease classifications, along with specific examples:
Infectious Diseases
- Tuberculosis (TB): Th1 cells and IFN-γ are crucial in controlling Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Deficiencies in Th1 cell-related molecules, such as IL-12, IL-12R, or IFN-γ, can lead to impaired immune responses and increased susceptibility to TB.
- Listeriosis: Th1 cells and IFN-γ are essential for combating Listeria monocytogenes infection. Inadequate Th1 cell differentiation or impaired IFN-γ production can result in severe and disseminated listeriosis.
Autoimmune Diseases
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Th1 cells have been implicated in the pathogenesis of MS. Increased Th1 cell infiltration into the central nervous system (CNS) leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IFN-γ, promoting demyelination and neuroinflammation.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Th1 cell-related cytokines, particularly IFN-γ and TNF-α, contribute to the chronic inflammation and joint destruction observed in RA. Th1 cells drive the activation of synovial fibroblasts and promote the production of matrix metalloproteinases and pro-inflammatory mediators.
Allergic and Asthmatic Disorders
- Allergic Asthma: Although Th2 cells are traditionally associated with allergic asthma, Th1 cells and their cytokines, such as IFN-γ, can also contribute to the disease pathogenesis. Th1/Th2 imbalance and dysregulated Th1 cell responses can exacerbate airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction.
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD): AD is characterized by a defective skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Th1 cells, along with Th2 and Th17 cells, contribute to the inflammatory processes in AD. Elevated levels of Th1-related cytokines, including IFN-γ, have been observed in AD lesions.
Cancer
- Melanoma: Th1 cells and their cytokines, particularly IFN-γ, play a crucial role in anti-tumor immune responses against melanoma. Th1 cells promote the activation of cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells, enhancing tumor cell killing and immune surveillance.
- Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Th1 cell-related cytokines, such as IFN-γ, have both anti-tumor and pro-tumor effects in CRC. While IFN-γ can exert anti-tumor effects by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and promoting immune responses, it can also contribute to tumor progression by inducing immune suppressive mechanisms.
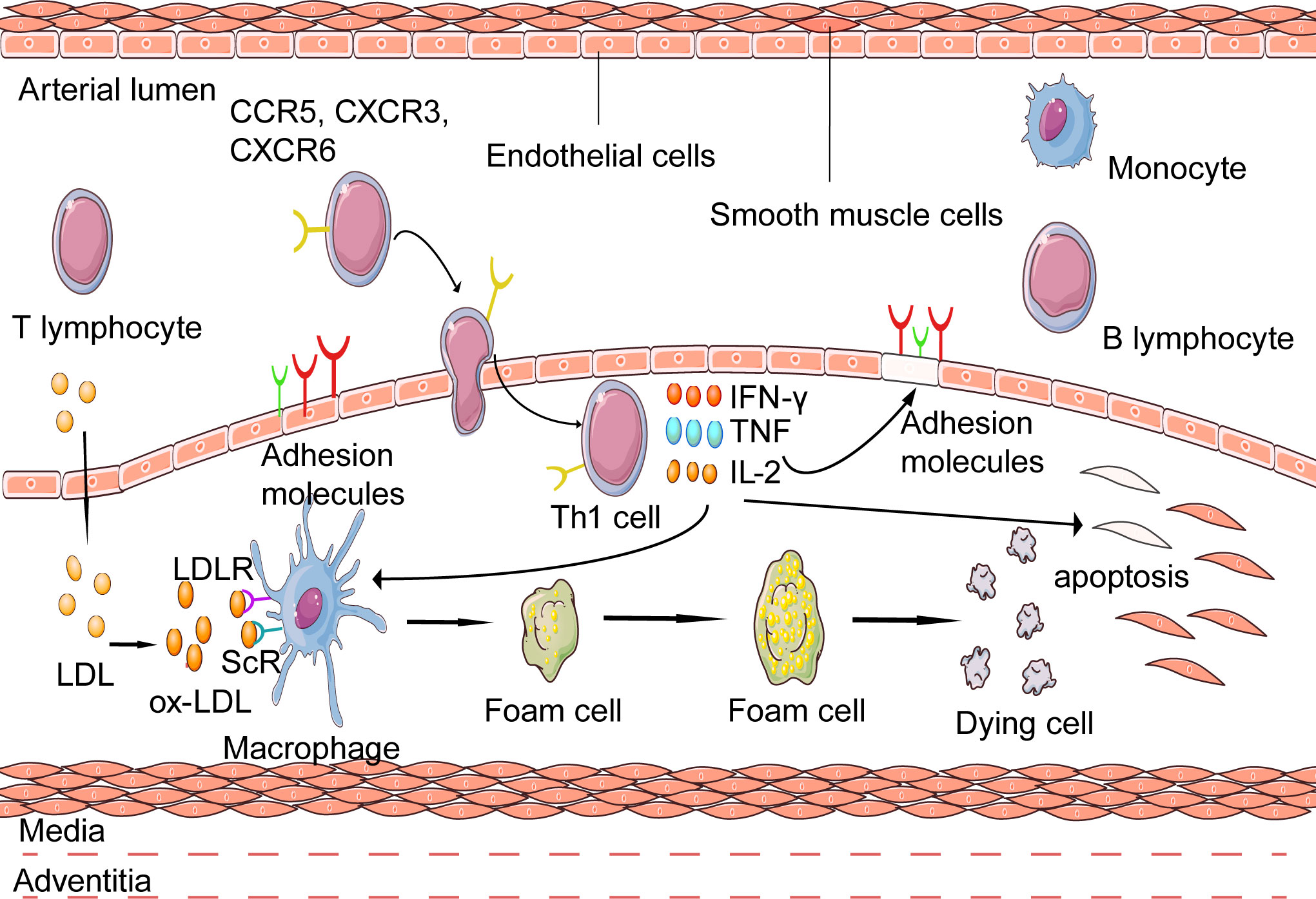 Fig.2 Activation of inflammatory response mediate by Th1 in atherosclerosis. (Chen J, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 Activation of inflammatory response mediate by Th1 in atherosclerosis. (Chen J, et al., 2023)
By offering a combination of high-quality products, tailored services, and valuable resources, Creative BioMart is committed to supporting Th1 cell research and fostering scientific breakthroughs in immunology, infectious diseases, autoimmunity, cancer, and beyond. Researchers can rely on Creative BioMart as a trusted partner in advancing our understanding of Th1 cell biology and its implications in health and disease. Visit our website or contact us today to learn more about our Th1 cell research resources and how we can support your scientific endeavors.
Related References
- Chen J, Xiang X, Nie L, et al. The emerging role of Th1 cells in atherosclerosis and its implications for therapy. Front Immunol. 2023;13:1079668.
- Romagnani S. Th1/Th2 cells. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 1999;5(4):285-294.

