FAS
-
Official Full Name
Fas cell surface death receptor -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor contains a death domain. It has been shown to play a central role in the physiological regulation of programmed cell death, and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various malignancies and diseases of the immune system. The interaction of this receptor with its ligand allows the formation of a death-inducing signaling complex that includes Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD), caspase 8, and caspase 10. The autoproteolytic processing of the caspases in the complex triggers a downstream caspase cascade, and leads to apoptosis. This receptor has been also shown to activate NF-kappaB, MAPK3/ERK1, and MAPK8/JNK, and is found to be involved in transducing the proliferating signals in normal diploid fibroblast and T cells. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, some of which are candidates for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). The isoforms lacking the transmembrane domain may negatively regulate the apoptosis mediated by the full length isoform. -
Synonyms
FAS;Fas cell surface death receptor;APT1;CD95;FAS1;APO-1;FASTM;ALPS1A;TNFRSF6
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Feline
- Cynomolgus
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Cattle
- Pig
- Sus scrofa (Pig)
- Bovine
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect cells
- Sf21 Cells
- Human
- CHO
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- T7
- MBP
Background
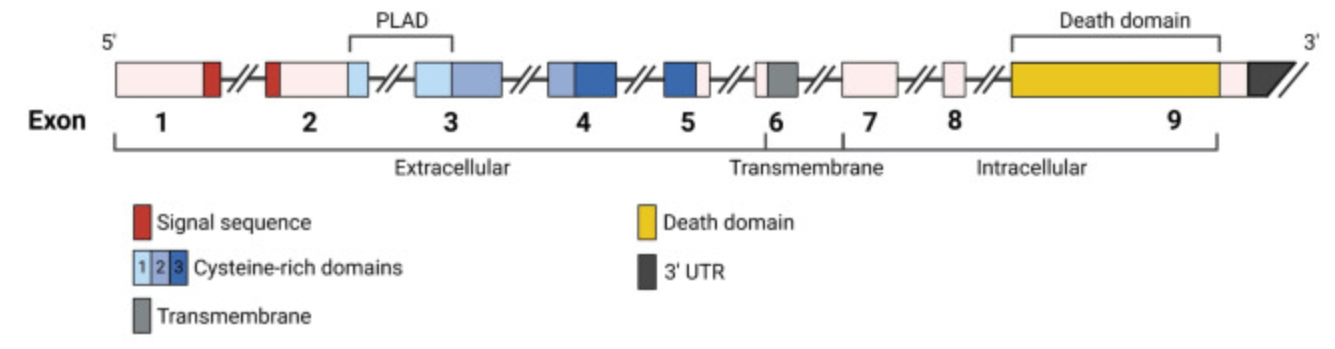
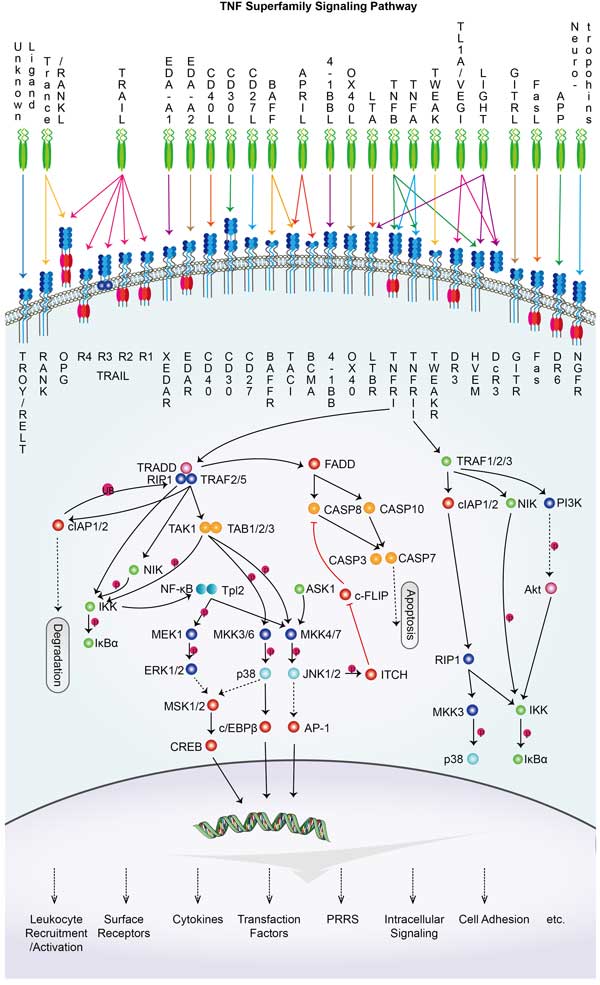
Fig1. Intron-exon structure of FAS gene delineating the exons coding for the extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular portions of FAS. (Filippo Consonni, 2022)
What is FAS protein?
FAS (Fas cell surface death receptor) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q23. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor contains a death domain. It has been shown to play a central role in the physiological regulation of programmed cell death, and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various malignancies and diseases of the immune system. The autoproteolytic processing of the caspases in the complex triggers a downstream caspase cascade, and leads to apoptosis. The FAS protein is consisted of 335 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 37.7 kDa.
What is the function of FAS protein?
FAS is a membrane protein that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Its function is mainly reflected in the regulation of apoptosis and immune response. When Fas binds to its ligand FasL, it activates the protease of the caspase family, triggering an intracellular apoptotic signaling pathway, leading to programmed cell death. This process is important for maintaining immune system homeostasis, removing damaged or abnormal cells, and preventing the development of tumors. In addition, Fas is involved in other biological processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration.
FAS Related Signaling Pathway
Fas (also called CD95/APO-1) is a cell surface death receptor that is mainly involved in signaling pathways associated with apoptosis. When Fas binds to its ligand FasL, it induces the formation of a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC), which in turn activates initiating caspases in the caspase family, such as Caspase-8 and Caspase-10. These activated caspases further activate downstream effector caspases, such as caspase-3, triggering the hydrolysis of a series of proteins, ultimately leading to the appearance of the typical morphological and biochemical features of apoptosis. In addition to its core role in the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, Fas signaling may also interact with other signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB pathway and the MAPK pathway, to play roles in inflammatory responses, cell proliferation, and immune regulation.
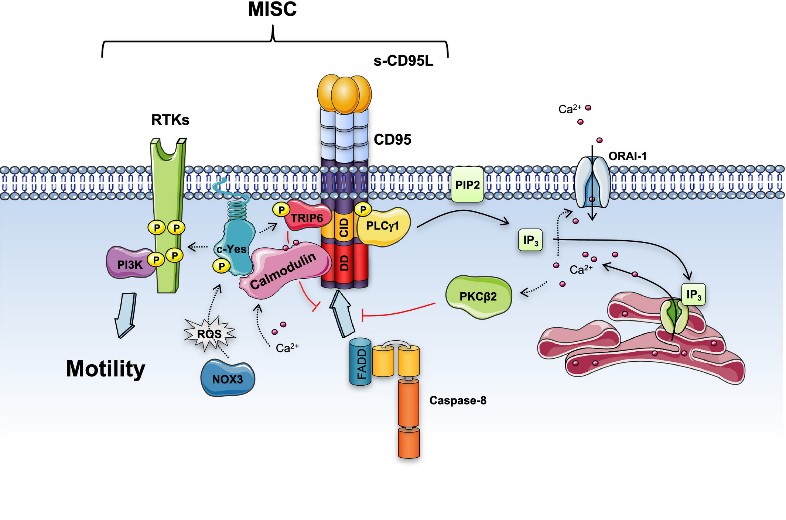
Fig2. Soluble CD95L triggers the Motility-induced Signaling Complex (MISC) formation. (Jean-Philippe Guégan, 2018)
FAS Related Diseases
Mutations or abnormal expression of Fas gene may lead to impairment of Fas mediated apoptosis mechanism, allowing immune cells that should die to survive, thus triggering autoimmune diseases. Certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma and leukemia, have been found to be associated with defects in the Fas signaling pathway. It may also be associated with myelosuppression, which affects blood cell production. Liver diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis, and neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis may also be associated with abnormal activity of Fas signaling pathways.
Bioapplications of FAS
On the clinical side, excitatory antibodies and antagonistic antibodies of Fas are being explored for tumor therapy and the treatment of autoimmune diseases. For example, inducing tumor cell apoptosis by activating the Fas pathway is a potential cancer treatment strategy. At the same time, inhibitors of the Fas pathway may play a role in preventing organ transplant rejection or treating certain autoimmune diseases.
Case Study
Case study 1: Laurent Gagnoux-Palacios, 2018
Finely tuned regulation of epithelial cell death maintains tissue integrity and homeostasis. At the cellular level, life and death decisions are controlled by environmental stimuli such as the activation of death receptors. We show that cell polarity and adherens junction formation prevent proapoptotic signals emanating from the Fas death receptor. Fas is sequestered in E-cadherin actin-based adhesion structures that are less able to induce downstream apoptosis signaling. Using a proteomic-based approach, we find that the polarity molecule Dlg1 interacts with the C-terminal PDZ-binding site in Fas and that this interaction decreases formation of the death-inducing complex upon engagement with Fas ligand (FasL), thus acting as an additional cell death protection mechanism. Thus E-cadherin and Dlg1 inhibit FasL-induced cell death by two complementary but partially independent mechanisms that help to maintain epithelial homeostasis by protecting normal polarized epithelia from apoptosis. When polarity is lost, the Fas-cadherin-Dlg1 antiapoptotic complex is disrupted, and FasL can promote the elimination of compromised nonpolarized cells.
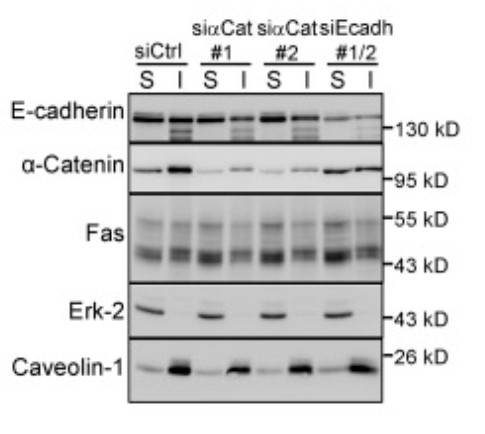
Fig1. Fas detergent solubility in HCT15 cells transfected by the indicated siRNAs was analyzed by IB.
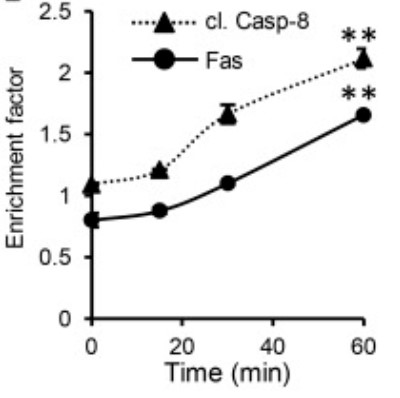
Case study 2: María Florencia Sánchez, 2018
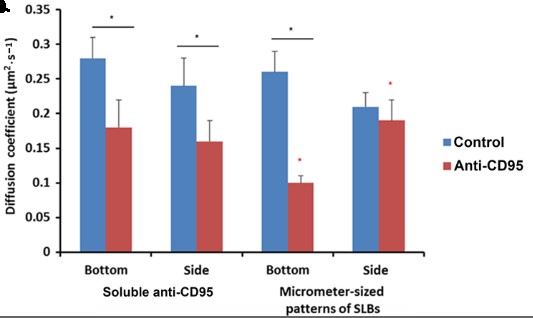
The cytotoxic synapse formed between cytotoxic T lymphocytes or natural killer cells expressing CD95L and target cells with CD95 on their surface is a key pathway for apoptosis induction by the immune system. Despite similarities with the immune synapse in antigen presenting cells, little is known about the role of the spatiotemporal organization of agonistic proteins/receptor interactions for CD95 signaling. Here, the researchers have developed an artificial cytotoxic synapse to examine how mobility and geometry of an anti-CD95 agonistic antibody affect receptor aggregation and mobility.
By measuring the distribution, diffusion coefficient, and fraction of immobile CD95 receptor in living cells, we show that at short times, the initial activation of CD95 occurs locally and is limited to the contact region of the cytotoxic synapse. This anisotropic activation of apoptotic signaling supports a role for confined interactions on the efficiency of signal transduction that may have implications for biomedical applications of extrinsic apoptosis induction.
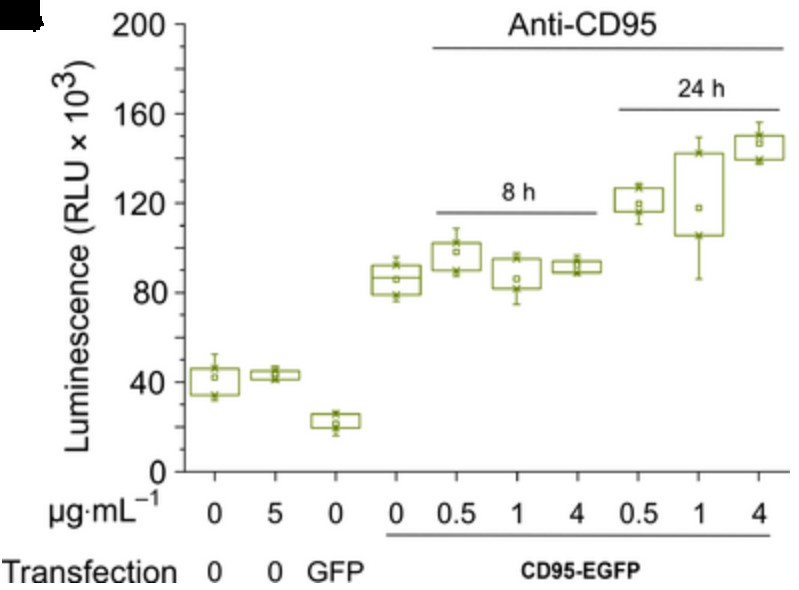
Fig3. Effector Caspases 3/7 activity measured by luminescence in CD95 ko T98G cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
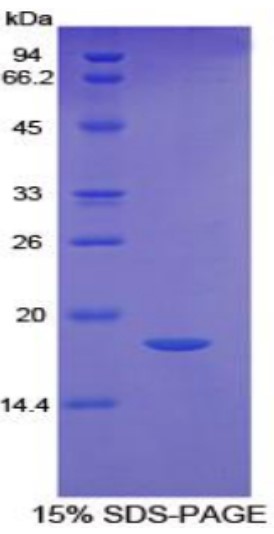
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FAS-614H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
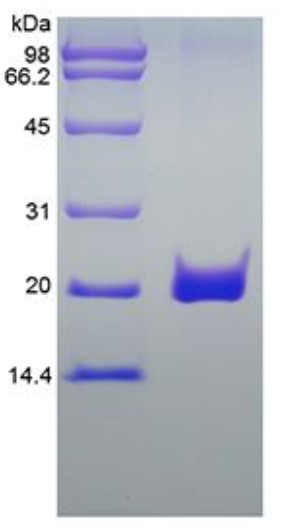
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FAS-26332TH) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
FAS involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FAS participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,p signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FAS were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Type I diabetes mellitus | HLA-DOB,HLA-G,HLA-DPB1,Fasl,TNF,HLA-DPA1,HLA-A,GZMB,INS2,CD80 |
| Autoi | HLA-DRB4,FASLG,IFNA6,PRF1,HLA-A,Il2,CD40LG,HLA-C,IFNA8,HLA-DRB5 |
| Herpes simplex infection | IFNB,SRPK1B,USP7,FOS,TRAF6,TNFRSF14,PVRL2,TAP2,C3A.3,TBPL1 |
| Allograft rejection | CD28,CD40,PRF1,IL12B,HLA-G,HLA-DPB1,MICA,HLA-F,HLA-E,H2-Q10 |
| Hepatitis B | STAT3,CXCL8,DDX3X,RAF1,Casp3,EGR2,Fasl,STAT1,IL6,MAP2K1 |
| Graft-versus-host disease | CD80,HLA-A,KLRD1,HLA-B,HLA-DRB1,CD86,TNF,H2-AA,HLA-DOA,HLA-DRB5 |
| TNF signaling pathway | BIRC2,AKT1,CASP8,CASP7,CFLAR,CXCL1,MAPK10,VCAM1,CASP10,MMP14 |
| Influenza A | FDPS,NXF1,IFNG,MAPK12,TRIM25,HLA-DPB1,Ifna11,IFNA5,IKBKE,IFNA13 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | RELA,PPM1AB,ATF4,PPP3R1B,NLK1,MOS,PDGFRA,HSPA2,MEF2CB,STK3 |
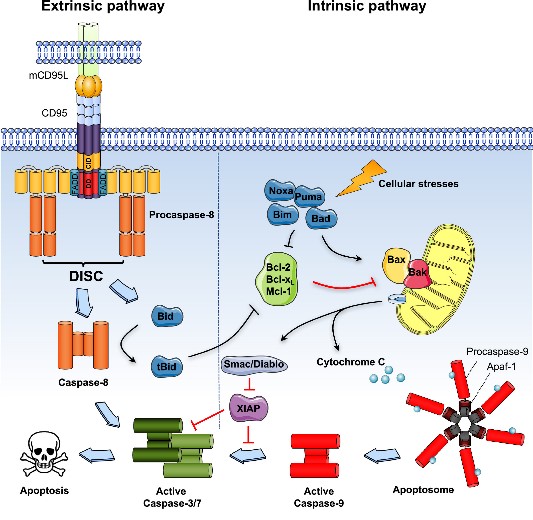
Fig1. Extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. (Jean-Philippe Guégan, 2018)
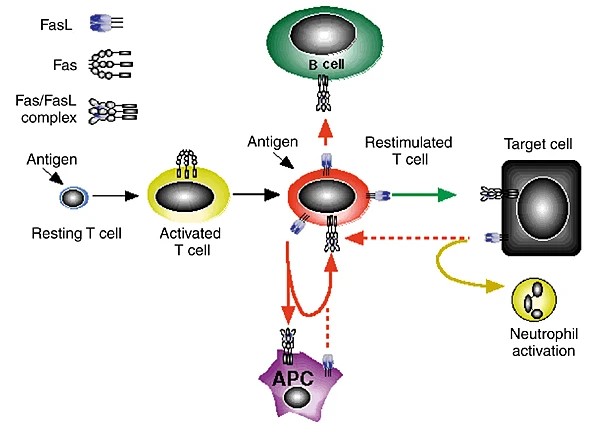
Fig2. Fas-FasL interactions mediate immune cell homeostasis. (R M Siegel, 2000)
Protein Function
FAS has several biochemical functions, for example, identical protein binding,kinase binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FAS itself. We selected most functions FAS had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FAS. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | SETD7,LDHAL6B,ACOT7,POLR2E,SCYL2,CORO1C,DDX18,CNOT6L,NEFM,APOA1BP |
| signal transducer activity | TAAR7D,AXIN1,TAAR14A,TRIM63,GNG2,TAS2R124,PTK2B,OXTRL,COPS2,GNA13A |
| tumor necrosis factor-activated receptor activity | TNFRSF19,TNFRSF11B,RELT,TNFRSF1A,TNFRSF1B,LTBR,Tnfrsf26,TNFRSF18,TNFRSF8,TNFRSF4 |
| receptor activity | EDAR,DERL1,AMFR,EIF2D,IL10RA,RNF139,NLGN2,ADCYAP1R1,TLR1,GFRA2A |
| kinase binding | PFKL,MOBKL1A,TRADD,BTG1,STUB1,CDC6,SIT1,C2orf44,PFKM,CTNNB1 |
| identical protein binding | MRI1,KHDC1B,SHARPIN,DCP1A,GBP5,SCAND1,CXADR,CCDC91,SNX8,IK |
Interacting Protein
FAS has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FAS here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FAS.
FADD
FAS Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
- Tumor Suppressors
- Adipocytokines
- Immune Regulatory Molecules on Endothelial Cells
- Cytokine and Growth Factor Receptors on VSMC
- Death Receptor–Ligand System
- Natural Killer Cell (NK Cell)
- gamma delta T Cells
- T Cell Markers
- CD Antigen (Neutrophils)
- CD Antigen (Helper T Cells)
- CD Antigen (Regulatory T Cells)
- TNF Receptor
- T Follicular Helper (Tfh) Cells
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Choi, BD; Jeong, SJ; et al. The Effect of Thymosin beta 4 for Osteoblast Adhesion on Titanium Surface. JOURNAL OF NANOSCIENCE AND NANOTECHNOLOGY 15:5663-5667(2015).
- Rutkowska, J; Bialek, M; et al. Differentiation of geographical origin of cream products in Poland according to their fatty acid profile. FOOD CHEMISTRY 178:26-31(2015).