CD Antigen (Helper T Cells)
Related Symbol Search List
- CD40 Ligand
- CD84
- CD48
- TNFRSF8
- TNFRSF9
- TNFSF9
- BAFF
- CD4
- LIGHT
- IL1R1
- CSF2RA
- Fas
- IFNGR1
- IL10RB
- IL13RA1
- IL7R
- IL18R1
- IL2RB
- TNFSF10
- TNFSF8
- CD70
- Ctla4
- IL13RA2
- IL17RA
- IL2RA
- IL2RG
- IL3RA
- IL4R
- IL5RA
- IL6ST
- TNFRSF1A
- TNFRSF1B
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CD Antigen (Helper T Cells) Research
Creative BioMart is your ultimate destination for all your research needs regarding CD antigens (helper T cells). Our carefully curated selection of products and personalized services are designed to support your exploration of the intricate world of helper T cells CD antigens and their crucial role in autoimmune and infectious diseases.
- Our product offerings include high-quality recombinant proteins, native proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, GMP proteins, assay kits, and more. Each product is meticulously tailored to meet your specific research requirements with unparalleled precision and expertise.
- Furthermore, we offer a wealth of resources on CD antigens (helper T cells), providing comprehensive insights into associated pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, relevant literature, and others.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD4-2219H | Recombinant Human CD4, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| CD48-10960H | Recombinant Human CD48 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CD70-891HA | Recombinant Human CD70 protein, Fc-tagged, APC labeled | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| TNFRSF8-563H | Recombinant Human TNFRSF8, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| TNFSF9-3323H | Recombinant Human TNFSF9, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CSF2RA-724H | Recombinant Human CSF2RA protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | human/IgG1/Fc |
| IFNGR1-2250H | Active Recombinant Human IFNGR1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CTLA4-01H | Active Recombinant Human CTLA4 Protein, His-Tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His |
| IL1R1-14174H | Recombinant Human IL1R1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL2RG-14197H | Recombinant Human IL2RG Protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IL6ST-3170H | Recombinant Human IL6ST protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
About CD Antigen (Helper T Cells)
Helper T cells, also known as CD4+ T cells, express specific clusters of differentiation (CD) antigens on their cell surface. These CD antigens serve as markers to identify and classify helper T cells, allowing for their distinction from other cell types within the immune system. The CD antigens associated with helper T cells play important roles in their development, activation, and function.
Here's an introduction to some of the CD antigens commonly associated with helper T cells:
- CD3: CD3 is a complex of proteins found on the surface of all T cells, including helper T cells. It is involved in signal transduction and T cell receptor (TCR) activation upon recognition of antigens. CD3 is essential for T cell development, maturation, and antigen responsiveness.
- CD4: CD4 is a glycoprotein expressed on the surface of helper T cells. It interacts with major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This interaction facilitates the binding of TCRs to the antigen-MHC-II complex, leading to T cell activation and the initiation of immune responses. CD4 also plays a role in the development and maintenance of regulatory T cells.
- CD28: CD28 is a co-stimulatory molecule expressed on helper T cells. It interacts with CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) molecules on APCs, providing an additional signal for T cell activation and effector functions. CD28 engagement enhances T cell proliferation, cytokine production, and survival.
- CD40 Ligand (CD154): CD40 Ligand is expressed on activated helper T cells. It binds to CD40, which is present on B cells, dendritic cells, and other APCs. This interaction is crucial for the activation of B cells, induction of immunoglobulin class switching, and antibody production.
- CD25: CD25, also known as interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain (IL-2Rα), is a marker associated with activated helper T cells. It is upregulated upon T cell activation and plays a role in IL-2 signaling. CD25 is essential for T cell proliferation, survival, and the development of regulatory T cells.
- CTLA-4: CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4) is a receptor expressed on activated helper T cells. It functions as an inhibitory receptor that competes with CD28 for binding to CD80 and CD86 on APCs. CTLA-4 negatively regulates T cell activation, helping to maintain immune homeostasis and prevent excessive immune responses.
These CD antigens associated with helper T cells are important for their identification, characterization, and classification within the immune system. They contribute to the precise functioning and regulation of helper T cells during immune responses, and they are also targets for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating immune activities in various diseases and conditions.
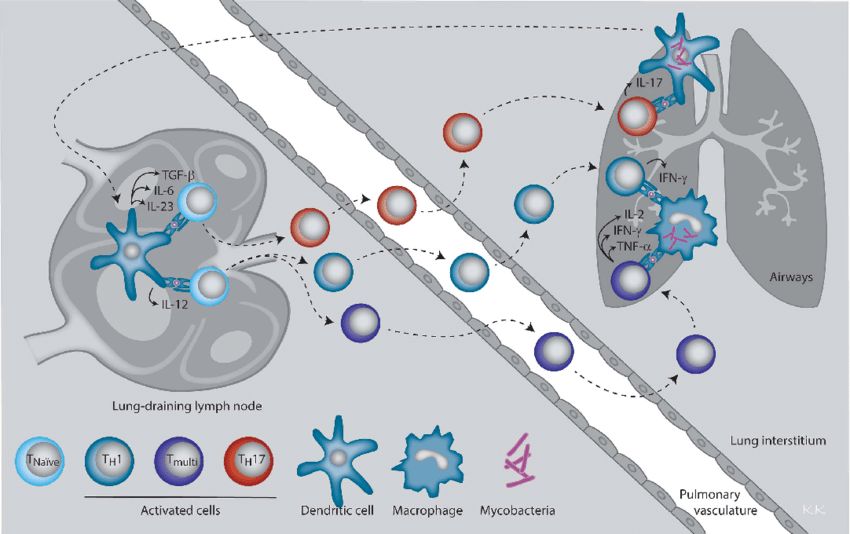 Fig.1 CD4 T helper subsets and their effector cytokines involved in immune protection against M. tuberculosis. (Kirman JR, et al., 2016)
Fig.1 CD4 T helper subsets and their effector cytokines involved in immune protection against M. tuberculosis. (Kirman JR, et al., 2016)
Classification of CD Antigen (Helper T Cells)
Helper T cells play a critical role in immune responses and can be classified into different subsets based on their cytokine production and immune regulatory functions:
- Th1 Cells: Produce cytokines like IFN-γ and IL-2. They promote cell-mediated immunity, activating macrophages and cytotoxic T cells to combat intracellular pathogens. Th1 responses are important in viral and bacterial infections and autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis.
- Th2 Cells: Produce cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. They are involved in antibody-mediated immunity, activating B cells and promoting allergic responses. Th2 responses defend against extracellular parasites and are associated with conditions like asthma and allergic rhinitis.
- Th17 Cells: Produce cytokines like IL-17 and IL-22. They contribute to inflammatory responses and defense against extracellular bacteria and fungi. Th17 cells are implicated in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
- Treg Cells: Regulatory T cells express the transcription factor Foxp3 and produce cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-β. They maintain immune tolerance, preventing excessive immune responses and suppressing immune activation. Treg dysfunction can lead to autoimmune diseases and allergies.
Helper T cell subsets are not always distinct and can exhibit plasticity, adapting their cytokine production based on signals received from the microenvironment.
Understanding the functions and classification of helper T cells is crucial for comprehending immune responses and developing targeted therapies for immune-related disorders.
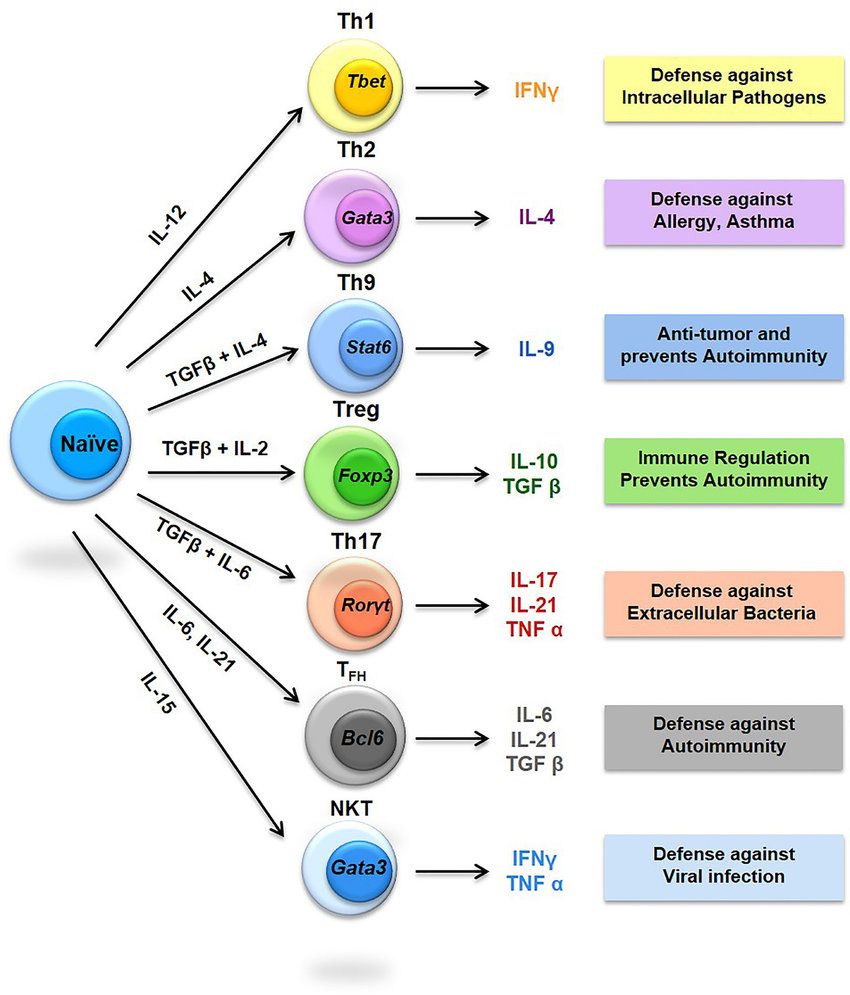 Fig.2 Diversity of T helper (Th) cells. (Srivastava RK, et al., 2018)
Fig.2 Diversity of T helper (Th) cells. (Srivastava RK, et al., 2018)
The role of CD Antigen (Helper T Cells) in Autoimmune and Infectious Diseases
CD antigens expressed on helper T cells play significant roles in both autoimmune and infectious diseases. Here's an overview of their involvement in these conditions:
Autoimmune Diseases
- CD4: In autoimmune diseases, CD4+ T cells can recognize self-antigens and initiate an immune response against the body's own tissues. These autoreactive CD4+ T cells can become activated and differentiate into effector T cells, leading to tissue damage and inflammation. Examples of autoimmune diseases where CD4+ T cells are involved include rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
- CD25 (IL-2Rα): Regulatory T cells (Tregs) express high levels of CD25 and are crucial for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmune responses. Dysfunction or reduced numbers of Tregs can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases by allowing autoreactive CD4+ T cells to escape regulation and cause tissue damage.
- CD40 Ligand (CD154): CD40 Ligand expressed on helper T cells plays a role in the activation of B cells and the production of autoantibodies in autoimmune diseases. Abnormal CD40 Ligand-CD40 signaling can contribute to the production of self-reactive antibodies and the development of diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren's syndrome.
Infectious Diseases
- CD4: Helper T cells are crucial in orchestrating immune responses against infectious pathogens. CD4+ T cells recognize antigens presented by infected cells or antigen-presenting cells and provide help to other immune cells, such as cytotoxic T cells and B cells, to eliminate the pathogen. In infectious diseases like HIV/AIDS, the human immunodeficiency virus specifically targets and infects CD4+ T cells, leading to their depletion and severe immunodeficiency.
- CD28: CD28 co-stimulation is required for optimal activation and expansion of CD4+ T cells during an immune response to infections. In the absence of CD28 signaling, T cell responses may be impaired, leading to decreased immune defense against pathogens.
- CTLA-4: CTLA-4 expressed on activated helper T cells negatively regulates T cell activation and prevents excessive immune responses. In infectious diseases, the modulation of CTLA-4 signaling can influence the balance between effective pathogen clearance and immunopathology. For example, in chronic viral infections like hepatitis C, upregulation of CTLA-4 can contribute to T cell exhaustion and immune dysfunction.
- CD3: CD3 complex is essential for T cell receptor (TCR) signaling and T cell activation during an immune response to infections. Disruption or dysfunction of CD3 signaling can impair T cell responses, affecting the clearance of pathogens.
The dysregulation or dysfunction of CD antigens and their associated signaling pathways can contribute to both autoimmune and infectious diseases.
Understanding the roles of these CD antigens in immune responses is crucial for the development of targeted therapies and interventions to modulate immune reactions in these conditions.
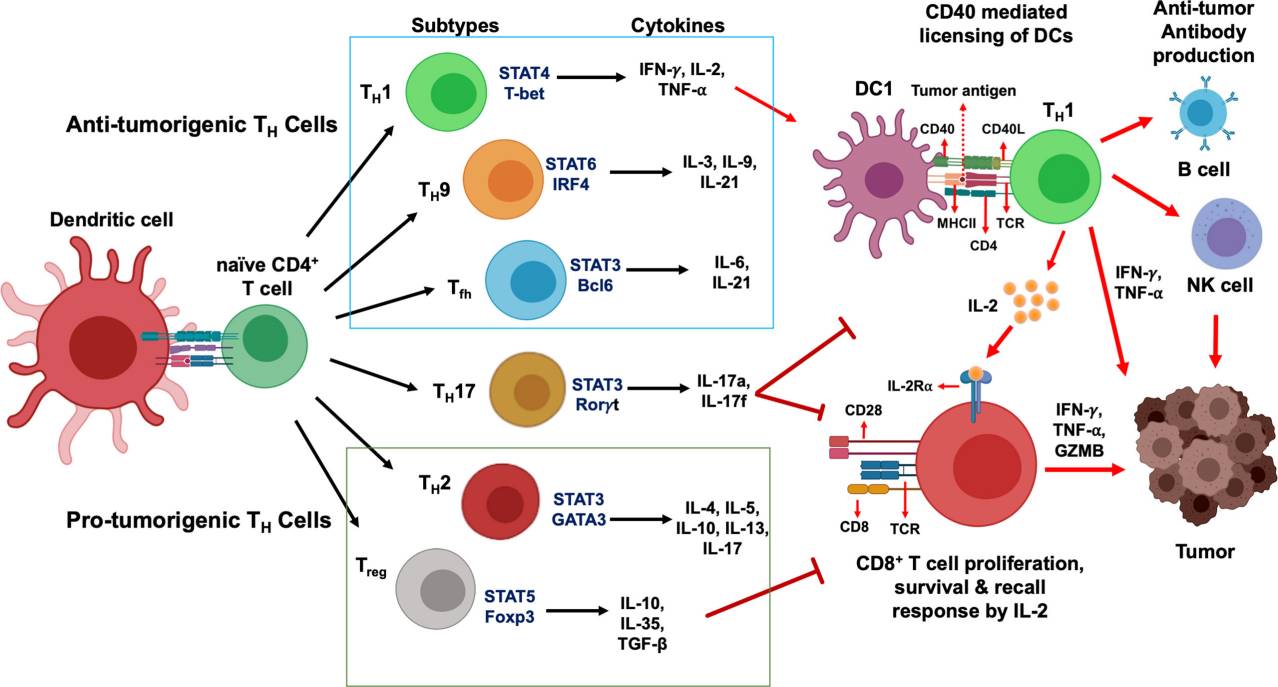 Fig.3 CD4+ T cells development and their functional subsets in immunity. (Basu A, et al., 2021)
Fig.3 CD4+ T cells development and their functional subsets in immunity. (Basu A, et al., 2021)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Srivastava RK, Dar HY, Mishra PK. Immunoporosis: Immunology of Osteoporosis-Role of T Cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:657.
- Basu A, Ramamoorthi G, Albert G, et al. Differentiation and regulation of TH cells: A balancing act for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Frontiers in immunology, 2021, 12: 669474.
- Kirman JR, Henao-Tamayo MI, Agger EM. The Memory Immune Response to Tuberculosis. Microbiol Spectr. 2016;4(6):10.1128/microbiolspec. TBTB2-0009-2016.

