Recombinant Human FAS, His & GST tagged
| Cat.No. : | FAS-281H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human FAS extracellular domain (Met 1-Glu 173) (NP_000034.1), fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus, was produced in Human Cell. |
| Availability | February 10, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Human Cells |
| Tag : | GST&His |
| Protein Length : | 1-173 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human Fas/Fc chimera is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein generated after removal of the signal peptide. The reduced monomer consists of 386 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 43.4 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the monomer migrates as an approximately 55-60 kDa protein due to glycosylation. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 eu per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Stability : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -70oC. |
| Storage : | Store it under sterile conditions at -20oC~-70oC. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution. Centrifuge the vial at 4℃ before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Publications : |
| Gene Name | FAS Fas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6) [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | FAS |
| Gene ID | 355 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000043 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000034 |
| MIM | 134637 |
| UniProt ID | P25445 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| FAS-4858HF | Recombinant Full Length Human FAS Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| FAS-203C | Recombinant Cynomolgus FAS | +Inquiry |
| FAS-547R | Recombinant Rat FAS protein(Met1-Lys170), hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Fas-618M | Recombinant Mouse Fas protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| FAS-1468R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque FAS Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| FAS-001CCL | Recombinant Cynomolgus FAS cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| FAS-1139RCL | Recombinant Rat FAS cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| FAS-2419MCL | Recombinant Mouse FAS cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| FAS-2185HCL | Recombinant Human FAS cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Soluble Fas affects erythropoiesis in vitro and acts as a potential predictor of erythropoiesis-stimulating agent therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease
Journal: American Journal of Physiology - Renal Physiology PubMed ID: 32003597 Data: 2021/4/1
Authors: Daniela Mendes Chiloff, Danilo Candido de Almeida, Miguel Angelo Goes
Article Snippet:Isolated CD34 + cells were seeded into Nunc four-well dishes (ThermoFisher Scientific) at a density of 1.0 × 10 5 cells/mL in 2 mL (per well) of methylcellulose-based Iscove’s modified DMEM containing FBS, BSA, human transferrin (iron-saturated), 2-mercaptoethanol, supplements, and the following recombinant human growth factors/cytokines: insulin, stem cell factor, IL-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and Epo (MethoCult GF 4434 Classic, STEMCELL Technologies).dishes (ThermoFisher Scientific) at a density of 1.0 × 10 5 cells/mL in 2 mL (per well) of methylcellulose-based Iscove’s modified DMEM containing FBS, BSA, human transferrin (iron-saturated), 2-mercaptoethanol, supplements, and the following recombinant human growth factors/cytokines: insulin, stem cell factor, IL-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and Epo (MethoCult GF 4434 Classic, STEMCELL Technologies). ... Cells were divided into 18 wells in 6 plates for CD34 + cells and incubated for 14 days ( 13 , 30 ) in the absence or presence of various levels of human recombinant sFas (FAS-FAS-281H, Creative BioMart).. We tested the effects of both 1 ) high levels (sFas-Hc group: 2, 4, and 8 ng/mL) and 2 ) low levels (sFas-Lc group: 0, 0.5, and 1 ng/mL) of sFas on CD34 + HSCs.We tested the effects of both 1 ) high levels (sFas-Hc group: 2, 4, and 8 ng/mL) and 2 ) low levels (sFas-Lc group: 0, 0.5, and 1 ng/mL) of sFas on CD34 + HSCs.
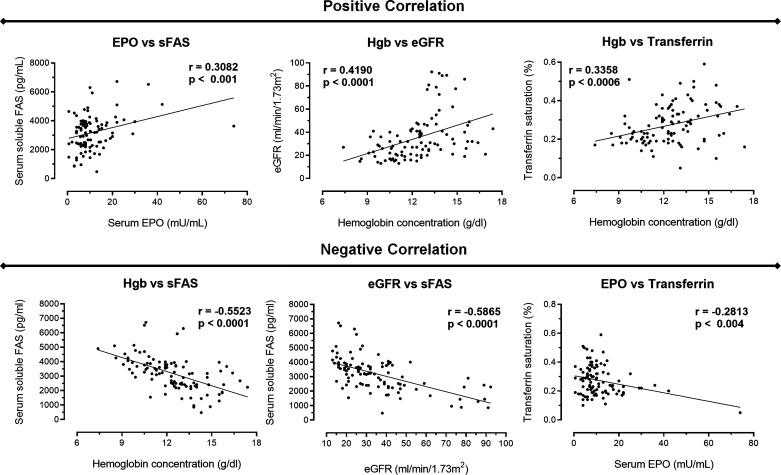
Global correlations between the variables analyzed. Correlations were performed using our data collection comprising 77 patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease patients with anemia and not submitted to erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA) therapy at baseline. We observed a positive correlation between serum erythropoietin (EPO) versus
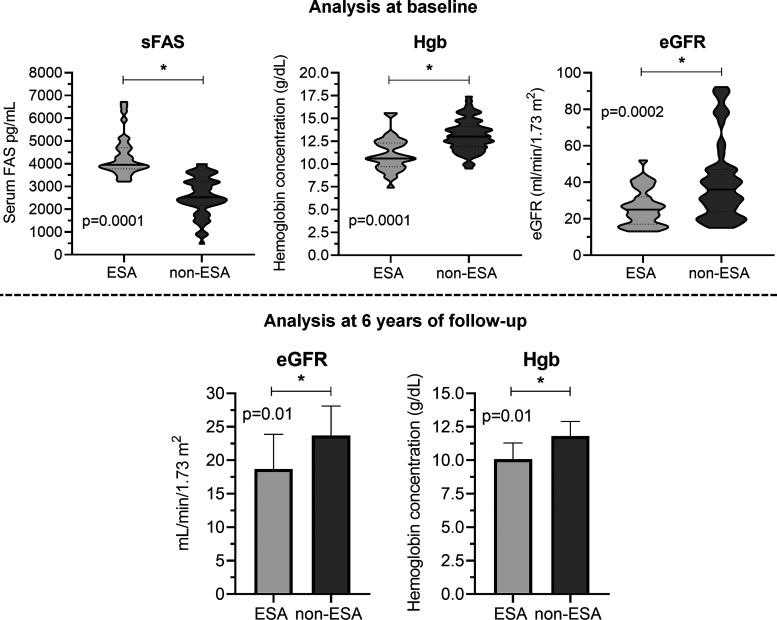
Direct comparison of
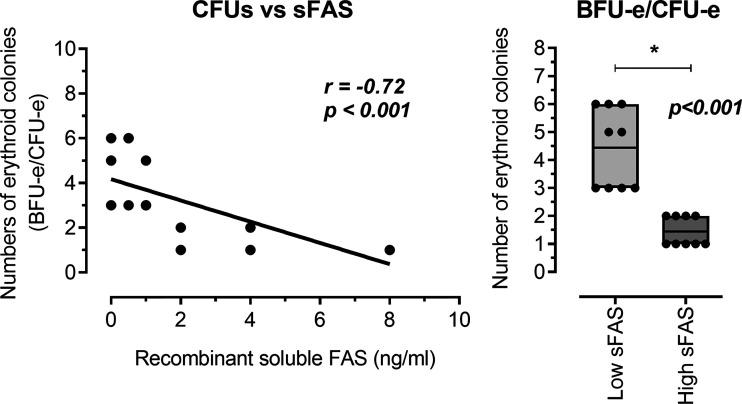
Analyze of the
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All FAS Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All FAS Products
Required fields are marked with *



