CD276
-
Official Full Name
CD276 molecule -
Overview
B7-H3 is a member of the B7 gene family. It has 88% amino acid sequence identity with mouse B7-H3. It is mostly expressed on professional APCs, including B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Its expression on dendritic cells appears to be up-regulat -
Synonyms
CD276;CD276 molecule;CD276 antigen;B7 H3;B7H3;B7RP 2;B7 homolog 3;costimulatory molecule;B7-H3;B7RP-2;4Ig-B7-H3
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Rat
- Monkey
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- HEK293
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- C-His
- C-hFc
- HEK293T
- Avi
- His
- mFc
- Fc
- GST
- Flag
- hIgG4
- Non
- EGFP
- mIgG2a
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is CD276 protein?
CD276 (CD276 molecule) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 15 at locus 15q24. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily, and thought to participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. Studies show that while the transcript of this gene is ubiquitously expressed in normal tissues and solid tumors, the protein is preferentially expressed only in tumor tissues. Additionally, it was observed that the 3' UTR of this transcript contains a target site for miR29 microRNA, and there is an inverse correlation between the expression of this protein and miR29 levels, suggesting regulation of expression of this gene product by miR29. The CD276 protein is consisted of 534 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 57.2 kDa.
What is the function of CD276 protein?
CD276 acts as an immune checkpoint molecule and is selectively expressed in both tumor cells and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. CD276 is implicated in the regulation of glucose uptake and metabolism in tumor cells, supporting the Warburg effect, which is a metabolic characteristic of cancer cells. CD276 promotes angiogenesis by stimulating the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is crucial for the growth and survival of tumors. While CD276 mRNA is broadly expressed in various tissues, protein expression is not ubiquitous, suggesting post-transcriptional regulation mechanisms. CD276 is a highly glycosylated protein, and its post-translational modifications, such as glycosylation, are important for its function and stability on the cell surface.
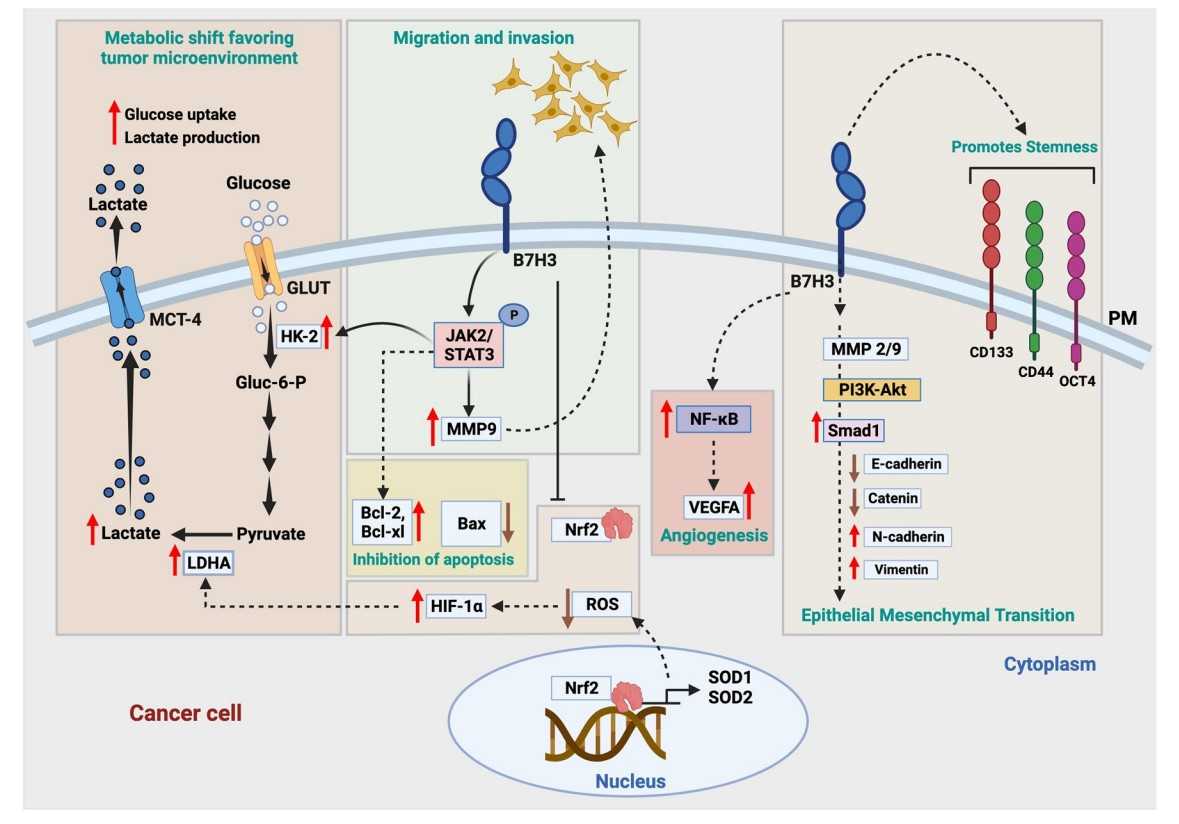
Fig1. The central role of B7-H3 on factors regulating tumor cell plasticity and tumorigenicity. (Elizabeth Varghese, 2024)
CD276 Related Signaling Pathway
CD276 has been shown to interact with the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathway, which is known to regulate cell survival, growth, and metabolism. Activation of this pathway by CD276 can lead to the suppression of immune cell activity and promotion of tumor cell survival. CD276 is mentioned as an immune checkpoint molecule in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathway, which is involved in the development and metastasis of carcinomas. CD276 has been linked to the regulation of metabolic pathways in tumor cells, which can support tumor growth and survival through altered energy metabolism. CD276 deletion in TAMs leads to downregulation of chemokine signaling pathways, which are important for immune cell recruitment and infiltration into the tumor.
CD276 Related Diseases
CD276 is highly expressed in bladder cancer and is linked to poorer overall survival and progression-free survival in patients. Its expression is associated with diminished tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and hastened cancer progression. Targeting CD276 has shown potential as a therapeutic strategy for bladder tumors. CD276 expression on tumor-associated endothelial cells in ovarian carcinoma is associated with poor patient outcomes. D276 is mentioned in the context of asthma, where it is associated with allergic diseases and the immune response. CD276 is associated with neuroblastoma, which is a cancer that arises from nerve cells, and is linked to the development and differentiation of neural crest cells. CD276 may play a role in this immune condition that occurs after a bone marrow transplant.
Bioapplications of CD276
CD276 blockade in combination with other immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4, is being explored to enhance the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy, particularly in tumors that do not respond well to single-agent treatments. Due to its elevated expression in various solid tumors and its role in promoting an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, CD276 is being explored as a therapeutic target. Monoclonal antibodies and bispecific antibodies targeting CD276 are being developed to disrupt its immunosuppressive functions.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Margie N Sutton, 2024
B7-H3 (CD276) has two isoforms (2Ig and 4Ig), no confirmed cognate receptor, and physiological functions that remain elusive. While differentially expressed on many solid tumors correlating with poor survival, mechanisms of how B7-H3 signals in cis (tumor cell) versus in trans (immune cell co-regulator) to elicit pro-tumorigenic phenotypes remain poorly defined. Herein, the researchers characterized a tumorigenic and signaling role for tumor cell-expressed 4Ig-B7-H3, the dominant human isoform, in gynecological cancers that could be abrogated upon CRISPR/Cas9 knockout of B7-H3; tumorigenesis was rescued upon re-expression of 4Ig-B7-H3. Size exclusion chromatography revealed dimerization states for the extracellular domains of both human 4Ig- and murine 2Ig-B7-H3. mEGFP lifetimes of expressed 4Ig-B7-H3-mEGFP fusions determined by FRET-FLIM assays confirmed close-proximity interactions of 4Ig-B7-H3 and identified two distinct homo-FRET lifetime populations, consistent with monomeric and homo-dimer interactions. In live cells, bioluminescence imaging of 4Ig-B7-H3-mediated split luciferase complementation showed dimerization of 4Ig-B7-H3.
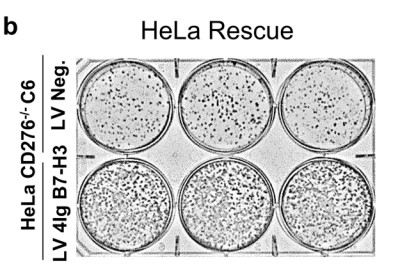
Fig1. HeLa CD276-/- cells engineered to re-express 4Ig-B7-H3 (LV B7-H3) or a negative vector control (LV Neg) were used to perform a clonogenic assay.
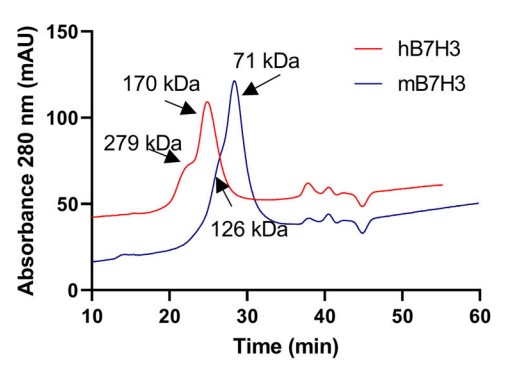
Fig2. Chromatograms of human 4Ig-B7-H3 and murine 2Ig-B7-H3 with their calculated molecular weights.
Case Study 2: Haiyan Jin, 2023
Ferroptosis, a newly discovered form of regulated cell death, has been reported to be associated with multiple cancers, including colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the underlying molecular mechanism is still unclear. In this study, the researchers identified B7H3 as a potential regulator of ferroptosis resistance in CRC. B7H3 knockdown decreased but B7H3 overexpression increased the ferroptosis resistance of CRC cells, as evidenced by the expression of ferroptosis-associated genes (PTGS2, FTL, FTH, and GPX4) and the levels of important indicators of ferroptosis (malondialdehyde, iron load). Moreover, B7H3 promoted ferroptosis resistance by regulating sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBP2)-mediated cholesterol metabolism. Both exogenous cholesterol supplementation and treatment with the SREBP2 inhibitor betulin reversed the effect of B7H3 on ferroptosis in CRC cells. Furthermore, the researchers verified that B7H3 downregulated SREBP2 expression by activating the AKT pathway. Additionally, multiplex immunohistochemistry was carried out to show the expression of B7H3, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2, and SREBP2 in CRC tumor tissues, which was associated with the prognosis of patients with CRC.
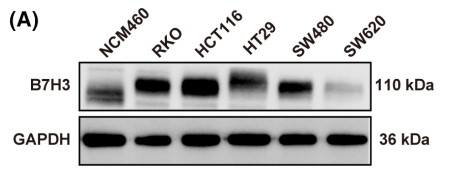
Fig3. B7H3 protein levels were analyzed by western blotting.
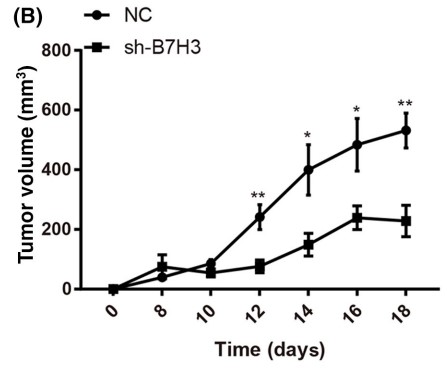
Fig4. Volumes of B7H3-knockdown HCT116 tumors in nude mice fed a high cholesterol diet.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD276-053H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD276-303H)
Involved Pathway
CD276 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD276 participated on our site, such as Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD276 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | Ntng2,NTNG1,CNTNAP2,SPN,CLDN10,BLB2,F11R.1,BLA,LRRC4C,CD58 |
Protein Function
CD276 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD276 itself. We selected most functions CD276 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD276. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor binding | PAOX,SEMA4D,RAB8B,DDX54,TNFSF12,GAS6,WNT2BA,PLAUR,CNPY3,TGFB2 |
| protein binding | BFAR,CCDC116,CASC3,NELL2,NEUROG1,PRMT1,RAB3IP,CCNG1,PKM,LSM3 |
Interacting Protein
CD276 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD276 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD276.
ganglioside_gm1;cona_canen
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wang, L; Kang, FB; et al. B7-H3-mediated tumor immunology: Friend or foe?. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CANCER 134:2764-2771(2014).
- Lutz, AM; Bachawal, SV; et al. Ultrasound Molecular Imaging in a Human CD276 Expression-Modulated Murine Ovarian Cancer Model. CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH 20:1313-1322(2014).
Reviews
We did see some binding .. which was a lot better than other VLPs we purchased from other companies.


