Other Monocytes/Macrophages CD Antigen
Related Symbol Search List
- ALCAM
- CD74
- CD84
- CD45
- L-selectin
- CD14
- CD16a
- FCGR3B
- FCGR4
- TLR1
- TLR2
- CD200R
- CD244
- ICAM-2
- Anpep
- Selplg
- CD68
- CSF1R
- CSF2RA
- L1CAM
- CD40
- CD64
- IL1R2
- PVR
- CD226
- IL10RB
- IL13RA1
- IL7R
- LAIR2
- Pvrl2
Immunology Background
Resources Available for Researching Other Monocyte/Macrophage CD Antigens
Creative BioMart's goal is to provide the global scientific research community with reliable products, customized services, and valuable resources related to other monocyte/macrophage CD antigens to promote the success of your research projects. We continually strive to provide the latest scientific research technologies and innovative solutions to meet your evolving research needs.
Our product line covers a wide range of monocyte/macrophage CD antigens, including cell adhesion molecules, receptors, receptor ligands, and immune system signaling molecules. We provide high-quality antibodies, recombinant proteins, chromatography reagents, and other related reagents to meet your experimental needs. Our products are strictly quality-controlled to ensure that you get reliable and consistent results. |
We also provide customized services to meet your specific research needs. Whether you need customized antibodies, recombinant proteins, or other related services, our professional team will provide you with efficient and accurate solutions. |
We also provide you with a series of resources related to other monocyte/macrophage CD antigens, including protein function, interacting proteins, related signal pathways, and other relevant topics. These resources will help you gain a deeper understanding of the functions, mechanisms of action, and importance of these antigens in different diseases and pathological processes. |
About Other Monocytes/Macrophages CD Antigen
Other monocyte/macrophage CD antigens play a crucial role in regulating immune responses and various functions. These antigens include cell adhesion molecules, receptors, receptor ligands, and signaling molecules involved in immune system communication. They play key roles in the normal function of monocytes/macrophages and in disease processes.
- Cell adhesion molecules such as ALCAM (activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule) and ICAM-2 (intercellular adhesion molecule-2) are widely expressed on the surface of monocytes/macrophages. They are involved in cell adhesion and interactions, regulating the migration and tissue localization of monocytes/macrophages.
- Receptors such as CD74, CD84, CD200R, CD244, CD226, IL1R2, IL10RB, IL13RA1, and IL7R are surface receptor molecules on monocytes/macrophages. They are essential for regulating cell activation, signaling, and immune modulation.
- Receptor ligands such as PVR (poliovirus receptor) and Pvrl2 (poliovirus receptor-like 2) are molecules on the surface of monocytes/macrophages that participate in cell-to-cell interactions and signaling, regulating cell activation and immune responses.
- Signaling molecules involved in immune system communication include CD45 (leukocyte common antigen), CD14, CD16a, FCGR3B, FCGR4, CD40, and CD64. They play important roles in cell activation, inflammation regulation, and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity processes.
These monocyte/macrophage CD antigens play significant roles in various diseases and pathological processes. For example, in inflammation, autoimmune diseases, infections, and tumors, abnormal expression or functional changes of these antigens may contribute to disease development and progression. Therefore, studying these antigens is crucial for a deeper understanding of monocyte/macrophage biology and the development of therapeutic approaches for related diseases.
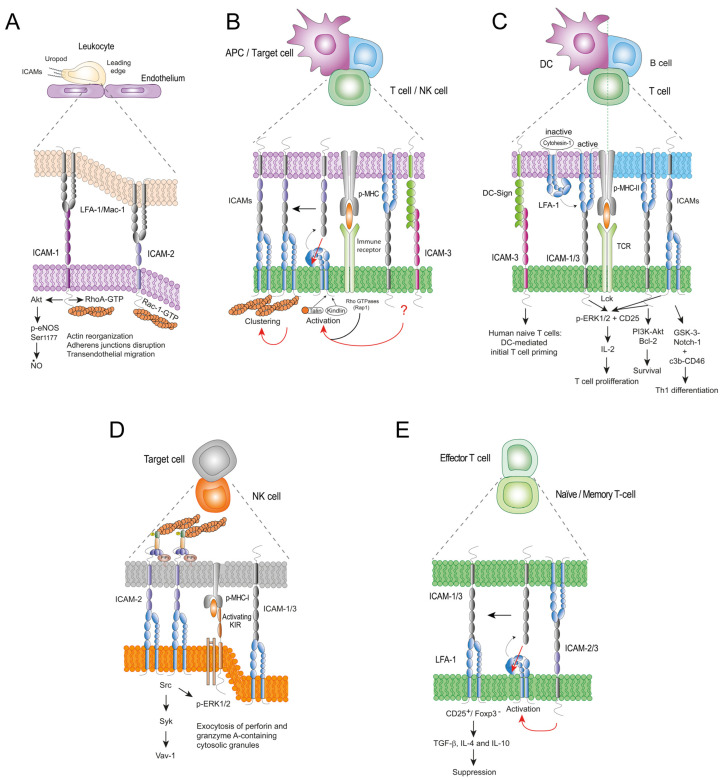 Fig.1 ICAMs-mediated cell-cell interactions in immunity. (Guerra-Espinosa C, et al., 2024)
Fig.1 ICAMs-mediated cell-cell interactions in immunity. (Guerra-Espinosa C, et al., 2024)
Role of Other Monocyte/Macrophage CD Antigens in Immune Responses
Other monocyte/macrophage CD antigens play a crucial role in immune cell recognition, activation, antigen presentation, and antigen response. These antigens are involved in various steps of the immune response, contributing to the effectiveness of immune cell function. Here are some key aspects of their importance:
Immune cell recognition
Monocyte/macrophage CD antigens facilitate the recognition of pathogens and foreign antigens by immune cells. For example, CD14 acts as a co-receptor for Toll-like receptors (TLRs), enabling the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on microbial pathogens. This recognition initiates immune responses and triggers the activation of immune cells.
Immune cell activation
CD antigens on monocytes/macrophages are essential for immune cell activation. They interact with ligands or other immune cells to transmit signals that activate monocytes/macrophages and promote their effector functions. For instance, CD40 on monocytes/macrophages interacts with CD40 ligand on T cells, leading to the activation of monocytes/macrophages and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Antigen presentation
Monocytes/macrophages play a critical role in antigen presentation, a process in which they capture, process, and present antigens to T cells. CD antigens on monocytes/macrophages, such as CD74, are involved in the presentation of antigens to CD4+ T cells through the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) pathway. This interaction is crucial for the activation of adaptive immune responses.
Antigen response
Monocyte/macrophage CD antigens also contribute to the antigen response by modulating immune cell functions. They can enhance or dampen immune responses depending on the specific CD antigen and its associated signaling pathways. For example, CD200R engagement on monocytes/macrophages inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby regulating immune responses and preventing excessive inflammation.
Understanding the importance of these monocyte/macrophage CD antigens in immune cell recognition, activation, antigen presentation, and antigen response is crucial for unraveling the complexities of the immune system and developing targeted immunotherapies. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which these antigens regulate immune responses and their potential as therapeutic targets.
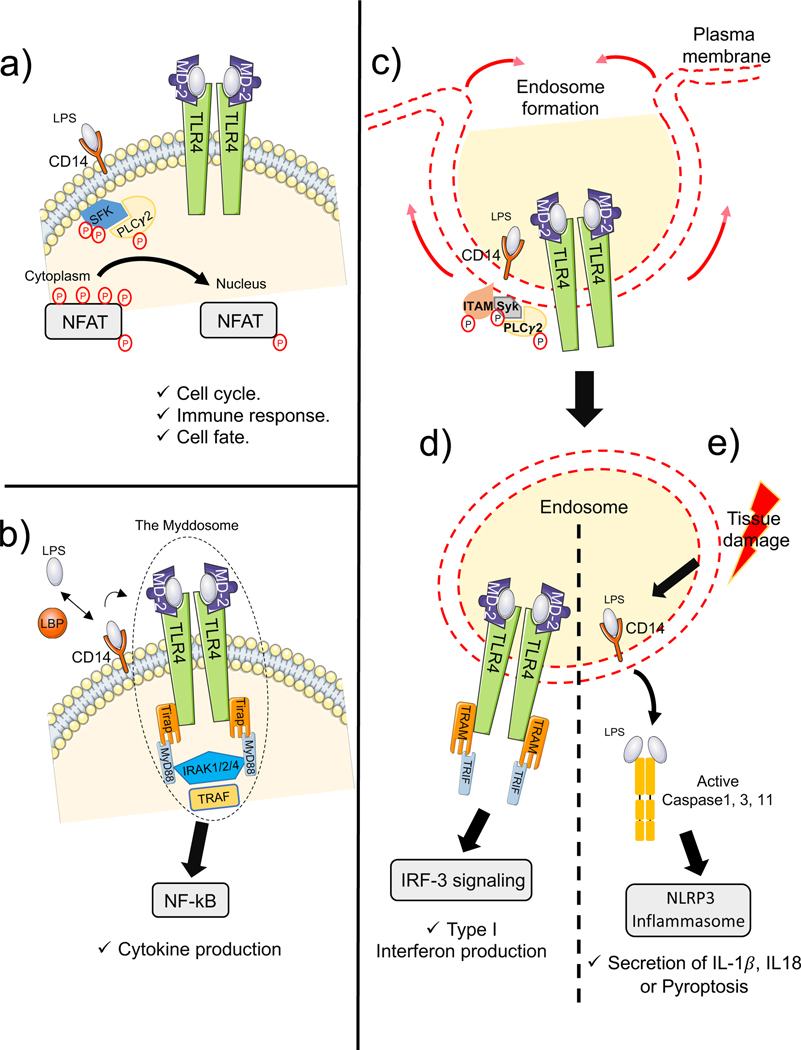 Fig.2 CD14 binds to Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and activates multiple signaling pathways. (Sharygin D, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 CD14 binds to Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and activates multiple signaling pathways. (Sharygin D, et al., 2023)
Role of Other Monocyte/Macrophage CD Antigens in Various Diseases and Pathological Processes
The role of other monocyte/macrophage CD antigens in various diseases and pathological processes is quite significant. These antigens are involved in regulating immune responses and can contribute to the development and progression of different diseases. Here are some examples:
Inflammation
Monocyte/macrophage CD antigens play a crucial role in the inflammatory response. Abnormal expression or dysregulation of these antigens can lead to chronic inflammation, which is associated with diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and atherosclerosis.
Autoimmune diseases
Dysregulation of monocyte/macrophage CD antigens can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases. For example, CD74 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis. CD200R is involved in regulating immune tolerance and its dysregulation has been associated with autoimmune conditions.
Infections
Monocytes/macrophages are key players in the immune response against infections. CD antigens on these cells are involved in recognizing and eliminating pathogens. Dysregulation of these antigens can impair the immune response and increase susceptibility to infections. For instance, CD16a and FCGR3B are important in antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity against pathogens, and their dysfunction can lead to increased susceptibility to infections.
Cancer
Monocytes/macrophages play dual roles in cancer development. On one hand, they can have anti-tumor effects by eliminating cancer cells. On the other hand, they can promote tumor growth and progression by creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment. CD antigens on monocytes/macrophages are involved in these processes. For example, CD40 is important for anti-tumor immune responses, while CD200R and CD244 can contribute to immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment.
Understanding the role of these monocyte/macrophage CD antigens in diseases and pathological processes is crucial for developing targeted therapies and interventions. Further research is needed to elucidate their precise mechanisms and explore their potential as therapeutic targets.
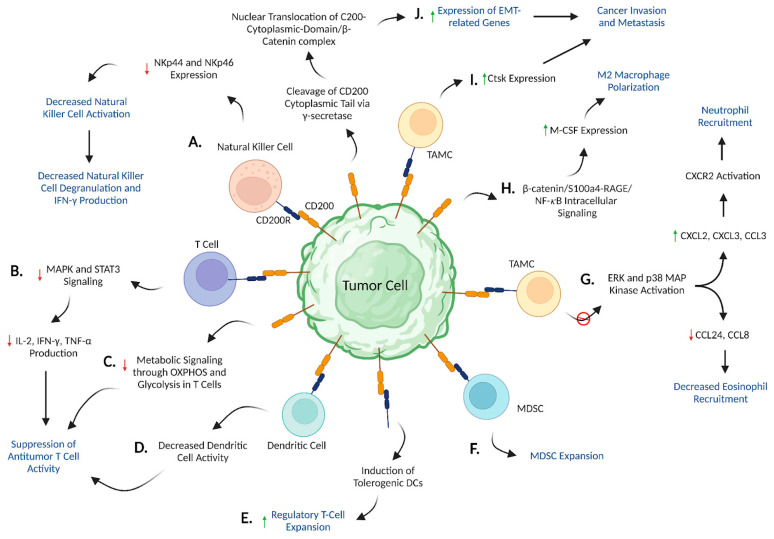 Fig.3 CD200/CD200R signaling promotes an immunosuppressive TME. (Nip C, et al., 2023)
Fig.3 CD200/CD200R signaling promotes an immunosuppressive TME. (Nip C, et al., 2023)
Understanding the role of these monocyte/macrophage CD antigens in diseases and pathological processes is crucial for developing targeted therapies and interventions. Further research is needed to elucidate their precise mechanisms and explore their potential as therapeutic targets.
If you have any questions or needs regarding our products, customized services, or resources, please feel free to contact our team of professionals. We look forward to working with you to advance scientific progress and innovation! Thank you for choosing Creative BioMart as your research partner!
Related References
- Guerra-Espinosa C, Jiménez-Fernández M, Sánchez-Madrid F, Serrador JM. ICAMs in Immunity, Intercellular Adhesion and Communication. Cells. 2024;13(4):339.
- Hullsiek R, Li Y, Snyder KM, et al. Examination of IgG Fc Receptor CD16A and CD64 Expression by Canine Leukocytes and Their ADCC Activity in Engineered NK Cells. Front Immunol. 2022;13:841859.
- Sharygin D, Koniaris LG, Wells C, Zimmers TA, Hamidi T. Role of CD14 in human disease. Immunology. 2023;169(3):260-270.
- Nip C, Wang L, Liu C. CD200/CD200R: Bidirectional Role in Cancer Progression and Immunotherapy. Biomedicines. 2023;11(12):3326.

