Wnt Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
- VANGL2
- FZD1
- FZD10
- FZD2
- Fzd4
- FZD5
- FZD6
- FZD9
- LRP1
- LRP10
- LRP11
- LRP8
- APOER2
- LRPAP1
- MUSK
- ROR1
- ROR2
- RYK
- ST7
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Wnt Receptors Research
At Creative BioMart you can find a wide range of products related to Wnt receptors, including recombinant proteins and other key products. In addition, we offer customized services to meet your specific requirements, ensuring you get the product you need.
In addition to our products and services, we offer a wealth of resources for your reference. Our resources cover all aspects of Wnt receptors, including the involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other relevant topics. These resources will be invaluable to researchers wishing to deepen their understanding of Wnt receptors and their role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
About Wnt Receptors
Wnt receptors are cell surface proteins that play a crucial role in receiving and transmitting signals from Wnt ligands to initiate intracellular signaling pathways. They include:
- Frizzled (Fz or Fzd): Seven-pass transmembrane receptors
- LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 (LRP5 and LRP6)
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-like Orphan Receptor-1/2 (ROR1/2)
- Related to tyrosine (Y) kinase (Ryk)
Other Wnt receptors and co-receptors include:
- Protein Tyr kinase 7 (PTK7)
- Muscle skeletal receptor Tyr kinase (MUSK)
- Proteoglycan families
Key Molecules in Wnt Receptors
Here are some key molecules involved in Wnt receptors, such as Wnt ligands, frizzled receptors, co-receptors, disheveled (DVL), β-catenin, Axin, TCF/LEF transcription factors, GSK3β. The intricate interactions and regulatory mechanisms involving these molecules contribute to the complexity and versatility of the Wnt signaling pathway. Further research continues to uncover additional components and mechanisms that modulate Wnt signaling and its implications in various biological processes.
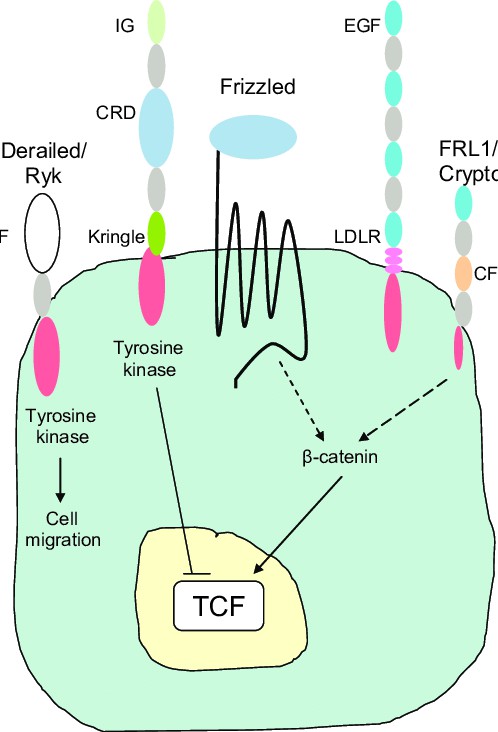 Fig.1 The different Wnt receptors on the cell membrane. (Laeremans H, et al., 2010)
Fig.1 The different Wnt receptors on the cell membrane. (Laeremans H, et al., 2010)
Functions of Wnt Receptors
The function of Wnt receptors is critical for receiving Wnt ligand signals and initiating intracellular signaling pathways. Here are the key functions of Wnt receptors:
- Wnt Ligand Binding: Wnt receptors, particularly FZD receptors, serve as the primary binding sites for Wnt ligands. The extracellular domains of FZD receptors interact with specific Wnt ligands, leading to the formation of a Wnt-receptor complex. This binding is essential for initiating downstream signaling events.
- Signal Transduction Initiation: Once Wnt ligands bind to their receptors, conformational changes occur in the receptors, triggering intracellular signaling cascades. These changes activate downstream signaling pathways and initiate intracellular responses.
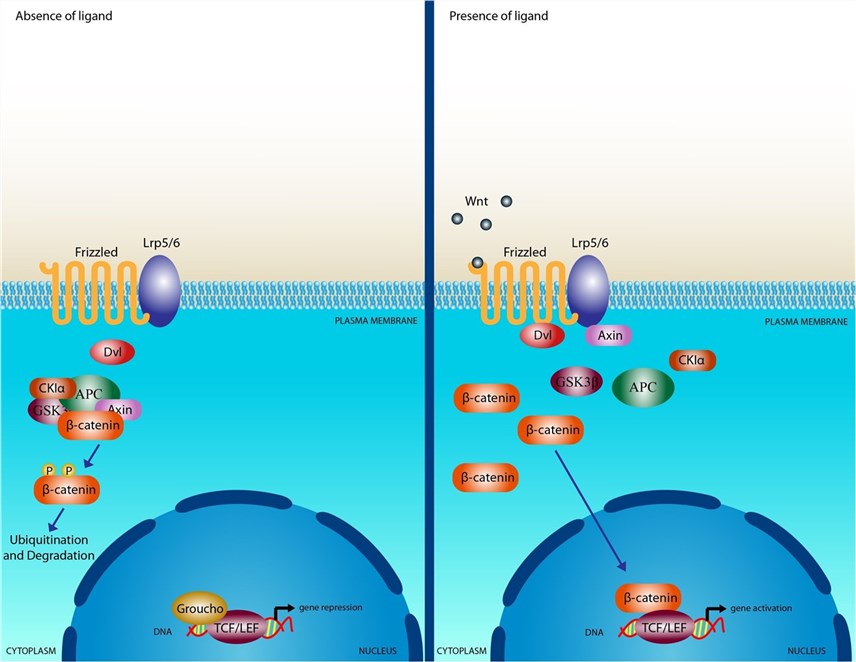
- Activation of Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway: FZD receptors, in conjunction with co-receptors like LRP5/6, play a key role in activating the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. In the absence of Wnt ligands, a destruction complex prevents the accumulation of β-catenin in the cytoplasm. However, when Wnt ligands bind to FZD receptors and co-receptors, it disrupts the destruction complex, allowing β-catenin to accumulate and translocate into the nucleus. In the nucleus, β-catenin interacts with transcription factors, leading to the transcription of target genes involved in various cellular processes.
- Activation of Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathways: Wnt receptors, including FZD receptors and co-receptors, are also involved in activating non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways. These pathways include the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway and the planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway. Non-canonical Wnt signaling regulates processes such as cell movement, tissue polarity, and cytoskeletal rearrangements.
- Cellular Responses and Developmental Processes: By initiating intracellular signaling pathways, Wnt receptors play crucial roles in numerous cellular responses and developmental processes. These include cell fate determination, cell proliferation, tissue homeostasis, tissue regeneration, neuronal development, synapse formation, stem cell maintenance, and organogenesis. Wnt receptors contribute to the regulation of these processes by transmitting Wnt signaling cues to the intracellular machinery.
- Disease Implications: Dysregulation of Wnt receptor signaling can have significant implications in various diseases. Abnormal activation or inhibition of Wnt receptors and the associated signaling pathways can contribute to developmental disorders, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other pathologies. Understanding the functions of Wnt receptors and their signaling pathways is crucial for unraveling the underlying mechanisms of these diseases and potentially developing therapeutic interventions.
Overall, Wnt receptors play pivotal roles in receiving Wnt ligand signals and triggering intracellular signaling pathways that regulate a wide array of cellular processes and developmental events.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- Laeremans H, Rensen SS, Ottenheijm HC, Smits JF, Blankesteijn WM. Wnt/frizzled signalling modulates the migration and differentiation of immortalized cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;87(3):514-523.
- Niehrs C. The complex world of WNT receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(12):767-779.

