Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, hFc-tagged
| Cat.No. : | ERBB2-41H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein(P04626-1)(Thr23-Thr652), fused with C-terminal hFc tag, was expressed in HEK293. |
| Availability | February 01, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | Thr23-Thr652 |
| Tag : | C-hFc |
| Form : | Lyophilized from 0.22μm filtered solution in PBS (pH 7.4). Normally 8% trehalose is added as protectant before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | Immobilized Human Her2, hFc Tag at 5μg/ml (100μl/well) on the plate. Dose response curve for Biotinylated Anti-Her2 Antibody , hFc Tag with the EC50 of 0.20μg/ml determined by ELISA. |
| Molecular Mass : | The protein has a predicted MW of 96.1 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 100-120 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| Endotoxin : | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE; > 95% as determined by HPLC |
| Storage : | Reconstituted protein stable at -80°C for 12 months, 4°C for 1 week. Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | Centrifuge tubes before opening. Reconstituting to a concentration more than 100 μg/ml is recommended. Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water. |
| Gene Name | ERBB2 v-erb-b2 erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog (avian) [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | ERBB2 |
| Synonyms | ERBB2; v-erb-b2 erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog (avian); NGL, v erb b2 avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2 (neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog); receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2; CD340; HER 2; HER2; NEU; herstatin; p185erbB2; proto-oncogene Neu; c-erb B2/neu protein; proto-oncogene c-ErbB-2; metastatic lymph node gene 19 protein; tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2; neuroblastoma/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog; v-erb-b2 avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2 (neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog); NGL; TKR1; HER-2; MLN 19; HER-2/neu; |
| Gene ID | 2064 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001005862 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001005862 |
| MIM | 164870 |
| UniProt ID | P04626 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ERBB2-14H | Active Recombinant Human ERBB2 Protein, Fc/His-tagged, Alexa Fluor® 647 conjugated | +Inquiry |
| ERBB2-6H | Recombinant Human ERBB2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Erbb2-6839R | Recombinant Rat Erbb2 Protein (Ala67-Val323), C-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| ERBB2-177HAF647 | Active Recombinant Human ERBB2 Protein, DDDDK-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated | +Inquiry |
| ERBB2-1216CAF555 | Recombinant Monkey ERBB2 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ERBB2-1727MCL | Recombinant Mouse ERBB2 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ERBB2-465HCL | Recombinant Human ERBB2 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ERBB2-343HKCL | Human ERBB2 Knockdown Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| ERBB2-2008RCL | Recombinant Rhesus ERBB2 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ERBB2-2658HCL | Recombinant Human ERBB2 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
In vitro Fab display: a cell-free system for IgG discovery
Journal: Protein Engineering, Design and Selection PubMed ID: 24586053 Data: 2014/4/1
Authors: Ryan L. Stafford, Marissa L. Matsumoto, Aaron K. Sato
Article Snippet:The coupled transcription/translation reactions were allowed to proceed for 60 min at 30°C.The coupled transcription/translation reactions were allowed to proceed for 60 min at 30°C.. The remaining selection was performed using standard protocols ( ) with 14 nM HER2/ErbB2 ECD (Creative BioMart) previously biotinylated.. Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR was performed using a one-step Transcriptor RT-PCR kit (Roche) with T7B/TolAk primers.Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR was performed using a one-step Transcriptor RT-PCR kit (Roche) with T7B/TolAk primers.
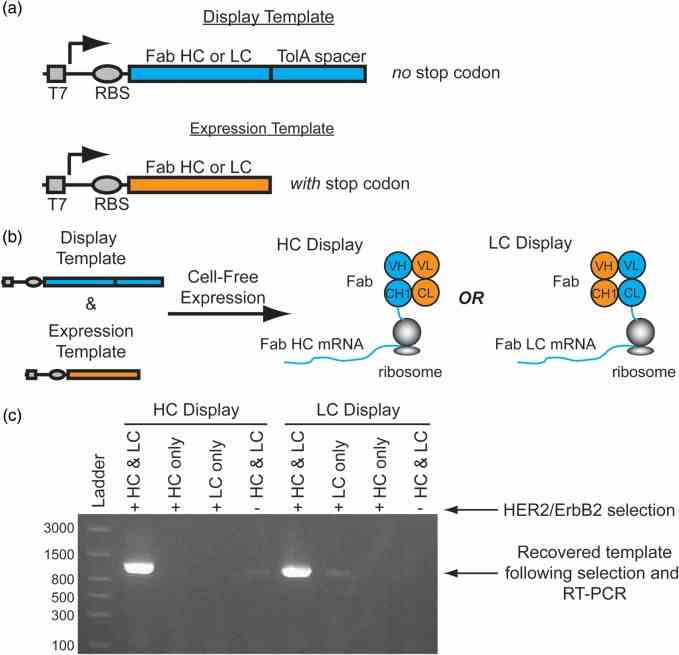
Conceptual overview of Fab display. ( a ) To display functional heterodimeric Fab domains from ribosomes two DNA templates are required for transcription: 1. A ‘Display Template’ lacking a stop codon at the end of a disordered TolA spacer, and 2. An ‘Expression Template’ with a stop codon. ( b ) A mixture of a display template and its complementary expression template co-expressed in a cell-free translation mixture enables the formation of a ternary complex of the functional Fab, ribosome and mRNA complex. For HC display, the HC display template is co-expressed with the LC expression template which enables the selection of a HC library. Alternatively, co-expression of the LC display template with the HC expression template enables LC display. ( c ) Co-expression of both the trastuzumab Fab HC and LC display and expression templates in either the HC or LC display format is required for significant recovery of the template following selection with
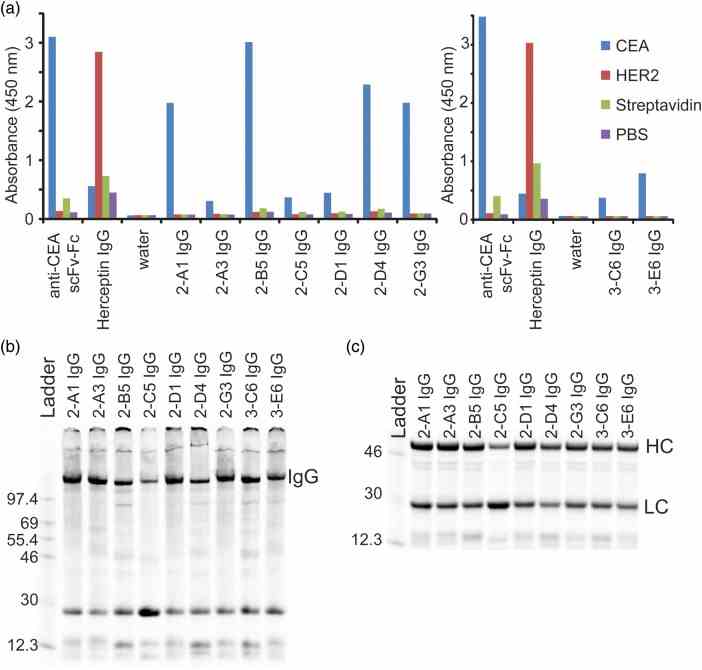
Screening and expression of IgGs with selected HCs. ( a ) IgGs from the selection were expressed on small scale (30 μl) in cell-free extract and screened by ELISA to find leads that were specific for CEA over
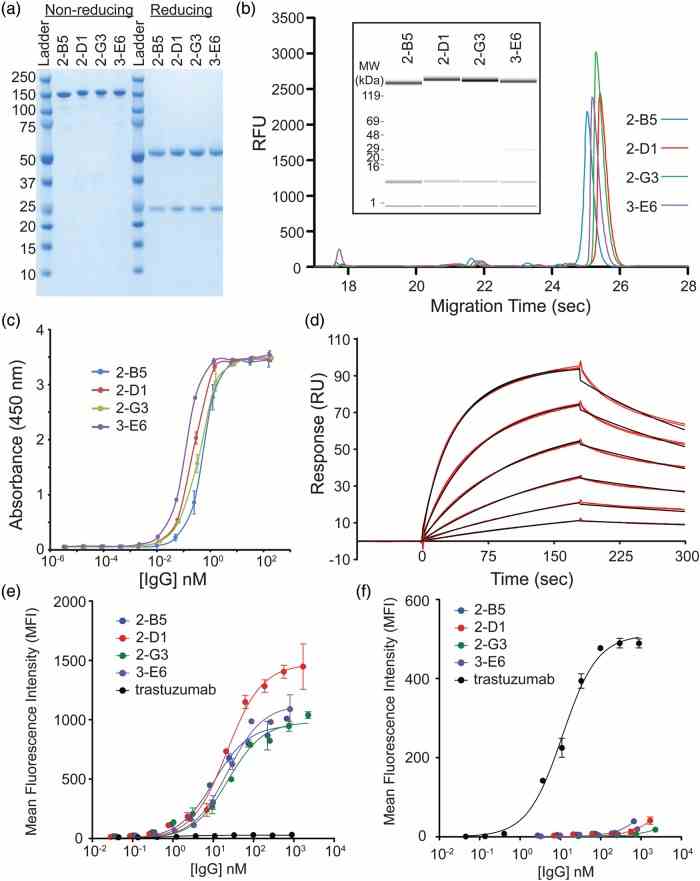
Characterization of purified IgGs. ( a ) The final purified anti-CEA IgGs run predominantly as a single band on a non-reducing SDS–PAGE gel consistent with the full-length IgG. Under reducing conditions, bands consistent with the HC and LC fragments are observed. ( b ) Caliper analysis reveals the high purity of the final IgGs. The inset shows the same sample traces where the amount of protein is indicated by the band intensity. ( c ) An ELISA of the purified anti-CEA IgGs have sub-nanomolar EC 50 values for CEA. ( d ) A sample Biacore trace (red lines) for the 2-G3 anti-CEA IgG and global fit to a bivalent binding model (black lines). Binding was measured in duplicate at 1.3, 2.5, 5.1, 10.1, 20.3 and 40.5 nM over three separate channels. A bivalent model fit the data better than simple 1 : 1 binding as expected for a bivalent IgG. ( e ) The reformatted IgGs show apparent high affinities on MKN45 cells which express high levels of CEA, while the wt trastuzumab (expressed in CHO) IgG does not. ( f ) The wt trastuzumab IgG (expressed in CHO) binds to the
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (1)
Ask a Question for All ERBB2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ERBB2 Products
Required fields are marked with *


