Interleukin (IL) superfamily
🧪 IL1RAPL1-776H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Fc
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-354 a.a.
🧪 IL1RAPL1-777H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Met1-Leu354
🧪 IL20RA-779H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag:
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Met 1-Lys 250
🧪 IL2RB-783H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Met1-Asp239
🧪 Il34-151M
Source: Human Cells
Species: Mouse
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-235 a.a.
🧪 IL6R-786H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 20-365 a.a.
🧪 IL6ST-787H
Source: E.coli
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Thr392~Leu566
🧪 LEPR-800H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Fc&His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-839 a.a.
🧪 IL4R-586H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:
🧪 IL17RA-2197H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Met1-Trp320
🧪 IL17RA-2199H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Fc&His
Conjugation: Biotin
Protein Length: Met1-Trp320
🧪 IL1R2-2200H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Phe14-Glu343
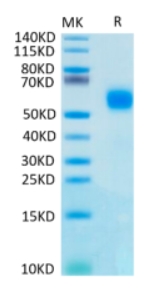
🧪 Il6st-2208M
Source: CHO
Species: Mouse
Tag: Fc&His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-617 a.a.
🧪 IL10RB-2251H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Met 1-Ser 220
🧪 IL13RA1-2252H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Ala27-Thr343
SubCategories
Interleukins—Product Overview
Interleukins (IL) are a diverse group of cytokines that play a critical role in the regulation of the immune system, mediating cell-to-cell communication and orchestrating immune responses. They are involved in a wide range of biological processes, including inflammation, cell proliferation and differentiation. As key modulators of immunity, interleukins have been extensively studied for their role in autoimmune diseases, infections and cancer.
Creative BioMart offers a comprehensive range of high-quality recombinant interleukins and related products to support research in immunology, inflammation and therapeutic development.
Jump to Section
Product Families
-
IL1 Family
-
IL6 Family
-
IL10 Family
-
IL12 Family
-
IL17 Family
-
Other Interleukins
-
IL1 Receptors
-
IL6 Receptors
-
IL10 Receptors
-
IL12 Receptors
-
IL17 Receptors
-
Other Interleukins Receptors
Background
The IL superfamily is a large group of cytokines that play essential roles in the regulation of immune responses, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. Primarily produced by leukocytes, ILs facilitate communication between immune cells, promote cell activation, and mediate host defense against infection. Each member of the IL family has distinct but often overlapping functions in immune modulation, tissue repair and disease pathogenesis, making them important targets for immunotherapy and biomedical research.
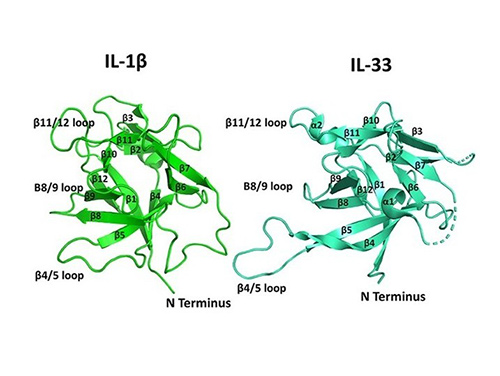
The interleukin superfamily comprises a diverse group of cytokines that share structural motifs and play important roles in immune regulation. Most interleukins are small, secreted proteins characterized by an α-helical bundle structure and are often grouped into families based on structural homology and receptor usage. Despite sequence differences, many interleukins form similar four-helix bundles and signal through specific receptor complexes, initiating pathways essential for inflammation, immunity and cellular communication.
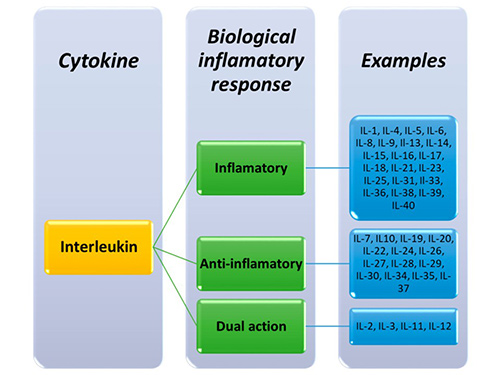
Interleukins are classified into different families based on their structure and function. More than 40 interleukins have been identified, each designated by a number (e.g., IL-1 to IL-40). Some interleukins, such as IL-2 and IL-7, promote immune cell growth, while others, such as IL-10 and IL-35, have anti-inflammatory properties. Each family interacts with specific receptors to trigger distinct signaling pathways that influence immune responses, inflammation, and tissue repair.
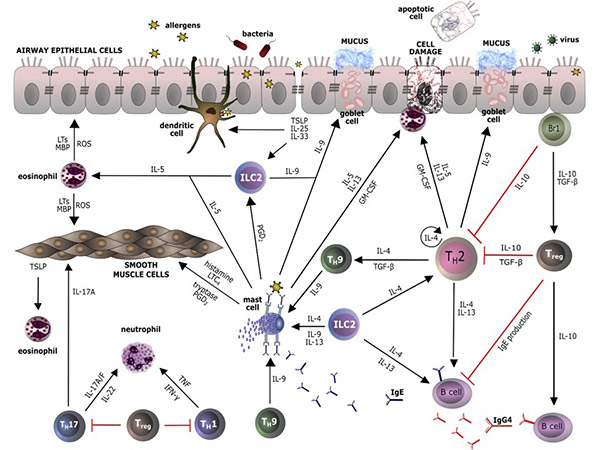
Interleukins regulate immune cell interactions by modulating responses to pathogens, stress, and injury. Pro-inflammatory interleukins, such as IL-1 and IL-6, promote immune activation, while anti-inflammatory interleukins, such as IL-4 and IL-10, suppress excessive immune responses to prevent tissue damage. They also play a role in adaptive immunity, influencing T-cell differentiation, antibody production and long-term immune memory to ensure a balanced and effective immune response.
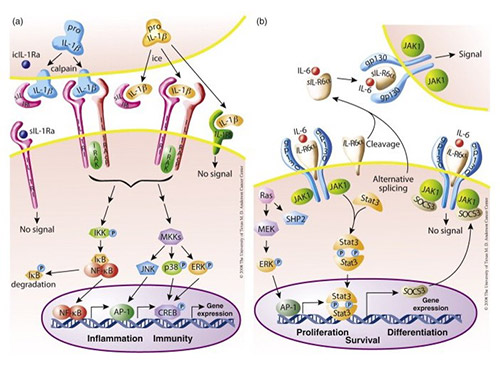
The interleukin signaling pathway consists of complex signaling cascades that regulate immune responses, inflammation, and cell communication. Upon binding to their specific receptors, interleukins activate intracellular signaling molecules such as the JAK-STAT, MAPK, and NF-κB pathways. These pathways induce gene expression changes that affect immune cell activation, differentiation, and cytokine production. Depending on the type of interleukin, signaling can either promote or suppress immune responses and plays a critical role in immunity, tissue repair, and disease progression, including autoimmunity, cancer, and infectious diseases.
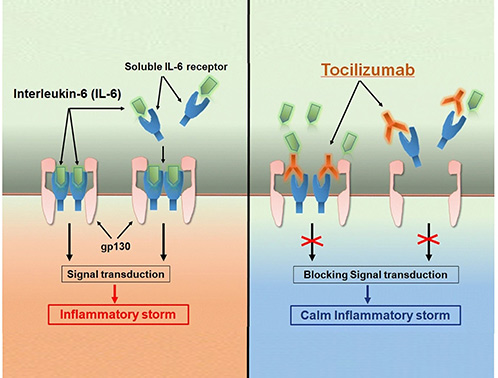
IL family-related drugs are biologic therapies designed to modulate immune responses by targeting specific IL cytokines or their receptors. These drugs are widely used to treat autoimmune, inflammatory, and allergic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and asthma. Examples include monoclonal antibodies like tocilizumab (anti-IL-6R) and ustekinumab (anti-IL-12/23), which block pro-inflammatory signaling and help restore immune balance in chronic inflammatory conditions.
Applications
Immunomodulation
Interleukins, such as IL-10 and IL-4, can be used to modulate the immune response. They are being tested to treat conditions such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases.
Vaccine Development
Some interleukins are used in vaccine development. They are used as adjuvants, substances that enhance the body's immune response to an antigen. For example, IL-12 is being studied for its potential use as an adjuvant in vaccines against several pathogens, including HIV.
Anti-Cancer Therapy
Some interleukins have been shown to have tumor suppressor properties. A classic example is the use of IL-2 in the treatment of certain cancers. More recent research is investigating interleukins such as IL-15 and IL-21 for their potential anti-cancer properties.
Diagnostics
Levels of certain interleukins can be used as diagnostic markers for certain conditions. For example, high levels of IL-6 are associated with systemic inflammation and can be used to predict outcomes in diseases such as sepsis and lung injury.
Treatment of Skin Disorders
Topical application of certain interleukins, such as IL-4 and IL-10, has shown potential to modulate local immune responses, reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms associated with chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema and atopic dermatitis, providing targeted therapeutic benefits.
Product Features
-
Broad Coverage of IL Family Members: Comprehensive collection from IL-1 to IL-38, including pro-inflammatory agonists, anti-inflammatory antagonists, and regulatory cytokines to support diverse research needs.
-
Multiple Expression Systems: Available in E. coli, mammalian, yeast, and insect cell expression systems to meet diverse post-translational modification and biofunctionality requirements.
-
Flexible Tag Formats: Interleukins offered with His, GST, or Fc tags, as well as untagged versions, enabling easier purification, detection, and downstream applications.
-
Species-Specific Variants: Human, mouse, rat, and other species versions available for cross-species studies and translational research.
-
Custom Production Services: Customized expression, formulation and bulk supply options to meet unique project or therapeutic development needs.
Case Study
Case 1: Autocrine IL-2 in Treg Homeostasis
Chawla AS, et al. A role for cell-autocrine interleukin-2 in regulatory T-cell homeostasis.
Activated T cells produce both interleukin-2 (IL2) and its high-affinity receptor component CD25. Regulatory CD4 T cells (Treg cells) do not make IL2, and the IL2-CD25 circuit is considered a paracrine circuit critical for their generation and maintenance. When the researchers revisited experiments with mixed bone marrow chimeras using a wide range of ratios of wild-type (WT) and IL2-/- genotype progenitors, they found that, as expected, thymic Treg cells were nearly equivalent between WT and IL2-/- genotypes at ratios with WT prominence. The data suggest that cell-intrinsic autocrine IL2 plays an important role in Treg generation and maintenance.
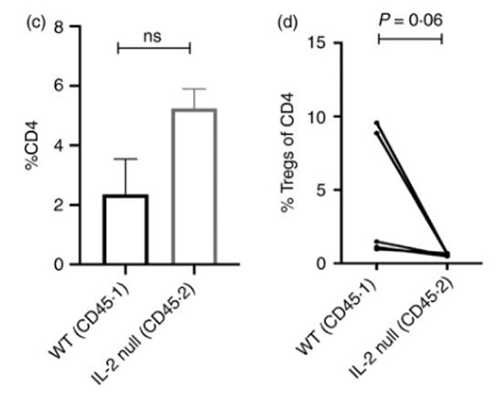
Figure 1. (c,d) For in vivo Treg generation, naive CD4 T‐cells (CD4+ CD25− CD44lo) cells from both WT and IL2−/− donor partners were isolated from mixed bone marrow chimeras and mixed in a 1:1 ratio and transferred into Rag−/− mice along with congenic WT Tregs. After 2 months, spleen cells from the Rag−/− recipients were analyzed for (c) CD4 expansion and (d) Treg induction from these donor populations.
Case 2: CXCL8 in Colorectal Cancer Outcomes
Li E, et al.CXCL8 associated dendritic cell activation marker expression and recruitment as indicators of favorable outcomes in colorectal cancer.
CXCL8 (IL-8) may also be a potential therapeutic target in cancer. CXCL8 is a potent chemotactic factor for neutrophils, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and monocytes, which are considered immunosuppressive components in cancer-bearing hosts. In this article, researchers identified the TME-related gene CXCL8 in a high-ImmuneScore population that contributed to better survival in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Their data suggested that targeting the CXCL8-CXCR2 axis might impede DC activation or recruitment, and this axis could be considered a favorable factor rather than a target for critical antitumor effects on CRC.
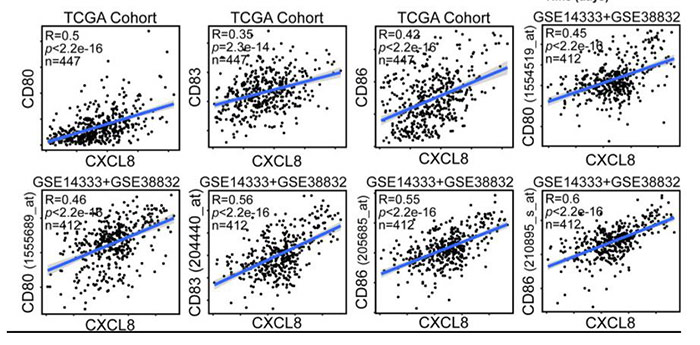
Figure 2. CXCL8 expression correlates with activated dendritic cells and their gene expression. Scatterplots representing the relationships between the expression of the dendritic cell activation genes CD80, CD83, and CD86 compared with CXCL8 expression in the TCGA cohort and GSE14333 and GSE38832 cohorts.
Case 3: CD14+ DC3s in Psoriasis Inflammation
Nakamizo S, et al. Single-cell analysis of human skin identifies CD14+ type 3 dendritic cells co-producing IL1B and IL23A in psoriasis.
Inflammatory skin diseases, including atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis (PSO), are underpinned by dendritic cell (DC)-mediated T cell responses. Currently, the heterogeneous human cutaneous DC population is incompletely characterized and its contribution to these diseases remains unclear. In this article, researchers performed index-sorted single-cell flow cytometry and RNA sequencing of lesional and nonlesional AD and PSO skin to identify macrophages and all DC subsets, including the newly described mature LAMP3+BIRC3+ DCs enriched for immunoregulatory molecules (mregDC) and CD14+ DC3. They found that CD14+ DC3s were increased in PSO lesional skin and co-produced IL1B and IL23A, which are pathological in PSO.
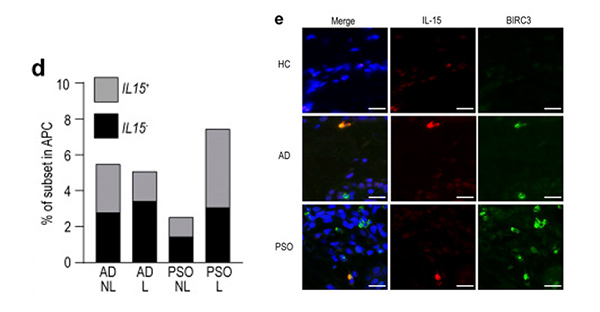
Figure 3. mregDCs produce IL-15 and are more abundant in AD skin. (d) Proportion of IL15-producing cells in AD and PSO skin. (e) Immunolabeling for IL-15 and BIRC3 in normal (n = 8), AD (n = 9), and PSO (n = 9) skin. Blue: DAPI, red: IL-15, green: BIRC3. Scale bar = 20 µm.
FAQs
-
Q: What is the interleukin (IL) superfamily?
A: The interleukin superfamily is a large group of cytokines that regulate immune responses, inflammation, hematopoiesis, and cell communication. Members range from IL-1 to IL-38, each with unique structures and biological functions, making them critical targets for research and therapeutic development. -
Q: What types of interleukin proteins do you offer?
A: We provide a wide range of high-purity recombinant interleukins, including individual IL family members like IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, IL-23, and more. Products are available in various species and tagged formats to meet diverse research and clinical needs.
-
Q: What are interleukin proteins used for in research?
A: Interleukins are widely used in immunology, cancer research, autoimmune disease modeling, and regenerative medicine. They help to study cytokine signaling pathways, immune cell regulation, inflammation, and potential targets for drug development.
-
Q: Are your IL proteins suitable for in vivo applications?
A: Yes, many of our interleukin products are endotoxin-free and produced under strict quality control, making them suitable for both in vitro and in vivo research applications. Technical Data Sheets are available for each product. -
Q: Can I request bulk quantities or custom formulations?
A: Absolutely! We support bulk orders and offer custom manufacturing services, including specific tags, carrier proteins, lyophilization, or formulation in buffers tailored to your research needs.

